Page 192 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 192
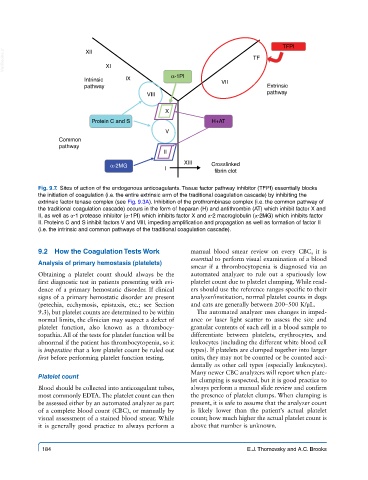
TFPI
VetBooks.ir XI TF
XII
Intrinsic IX α-1PI VII
pathway Extrinsic
VIII pathway
X
Protein C and S H+AT
V
Common
pathway
II
XIII
α-2MG Crosslinked
I fibrin clot
Fig. 9.7. Sites of action of the endogenous anticoagulants. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) essentially blocks
the initiation of coagulation (i.e. the entire extrinsic arm of the traditional coagulation cascade) by inhibiting the
extrinsic factor tenase complex (see Fig. 9.3A). Inhibition of the prothrombinase complex (i.e. the common pathway of
the traditional coagulation cascade) occurs in the form of heparan (H) and antithrombin (AT) which inhibit factor X and
II, as well as α-1 protease inhibitor (α-1PI) which inhibits factor X and α-2 macroglobulin (α-2MG) which inhibits factor
II. Proteins C and S inhibit factors V and VIII, impeding amplification and propagation as well as formation of factor II
(i.e. the intrinsic and common pathways of the traditional coagulation cascade).
9.2 How the Coagulation Tests Work manual blood smear review on every CBC, it is
essential to perform visual examination of a blood
Analysis of primary hemostasis (platelets)
smear if a thrombocytopenia is diagnosed via an
Obtaining a platelet count should always be the automated analyzer to rule out a spuriously low
first diagnostic test in patients presenting with evi- platelet count due to platelet clumping. While read-
dence of a primary hemostatic disorder. If clinical ers should use the reference ranges specific to their
signs of a primary hemostatic disorder are present analyzer/institution, normal platelet counts in dogs
(petechia, ecchymosis, epistaxis, etc.; see Section and cats are generally between 200–500 K/μL.
9.3), but platelet counts are determined to be within The automated analyzer uses changes in imped-
normal limits, the clinician may suspect a defect of ance or laser light scatter to assess the size and
platelet function, also known as a thrombocy- granular contents of each cell in a blood sample to
topathia. All of the tests for platelet function will be differentiate between platelets, erythrocytes, and
abnormal if the patient has thrombocytopenia, so it leukocytes (including the different white blood cell
is imperative that a low platelet count be ruled out types). If platelets are clumped together into larger
first before performing platelet function testing. units, they may not be counted or be counted acci-
dentally as other cell types (especially leukocytes).
Many newer CBC analyzers will report when plate-
Platelet count
let clumping is suspected, but it is good practice to
Blood should be collected into anticoagulant tubes, always perform a manual slide review and confirm
most commonly EDTA. The platelet count can then the presence of platelet clumps. When clumping is
be assessed either by an automated analyzer as part present, it is safe to assume that the analyzer count
of a complete blood count (CBC), or manually by is likely lower than the patient’s actual platelet
visual assessment of a stained blood smear. While count; how much higher the actual platelet count is
it is generally good practice to always perform a above that number is unknown.
184 E.J. Thomovsky and A.C. Brooks