Page 193 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 193
blood smear evaluation Blood smear evaluation function, including things like vWF release from the
allows for detection of platelet clumps, manual platelets or endothelial cells. To perform a BMBT,
VetBooks.ir estimation of platelet numbers, and evaluation of the patient’s upper lip is tied back to expose the
inner mucosal surface; mild sedation may be
platelet morphology. The feathered edge and body
of the smear are first scanned for frequent platelet
patient temperament. Using a commercially availa-
clumps. If clumping is present, all manual and required to facilitate the procedure depending on
automated estimates should be viewed as mini- ble spring loaded lancet, a small standardized inci-
mums that will underestimate the true value. sion is made on the inside of the lip at the level of
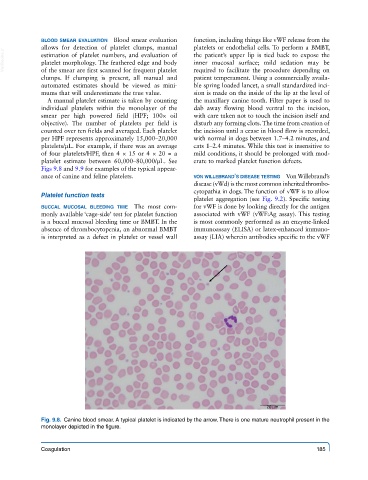
A manual platelet estimate is taken by counting the maxillary canine tooth. Filter paper is used to
individual platelets within the monolayer of the dab away flowing blood ventral to the incision,
smear per high powered field (HPF; 100× oil with care taken not to touch the incision itself and
objective). The number of platelets per field is disturb any forming clots. The time from creation of
counted over ten fields and averaged. Each platelet the incision until a cease in blood flow is recorded,
per HPF represents approximately 15,000–20,000 with normal in dogs between 1.7–4.2 minutes, and
platelets/μL. For example, if there was an average cats 1–2.4 minutes. While this test is insensitive to
of four platelets/HPF, then 4 × 15 or 4 × 20 = a mild conditions, it should be prolonged with mod-
platelet estimate between 60,000–80,000/μL. See erate to marked platelet function defects.
Figs 9.8 and 9.9 for examples of the typical appear-
ance of canine and feline platelets. von willebrand’s disease testing Von Willebrand’s
disease (vWd) is the most common inherited thrombo-
cytopathia in dogs. The function of vWF is to allow
Platelet function tests
platelet aggregation (see Fig. 9.2). Specific testing
buccal mucosal bleeding time The most com- for vWF is done by looking directly for the antigen
monly available ‘cage-side’ test for platelet function associated with vWF (vWF:Ag assay). This testing
is a buccal mucosal bleeding time or BMBT. In the is most commonly performed as an enzyme-linked
absence of thrombocytopenia, an abnormal BMBT immunoassay (ELISA) or latex-enhanced immuno-
is interpreted as a defect in platelet or vessel wall assay (LIA) wherein antibodies specific to the vWF
20 m
Fig. 9.8. Canine blood smear. A typical platelet is indicated by the arrow. There is one mature neutrophil present in the
monolayer depicted in the figure.
Coagulation 185