Page 2160 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2160
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation 1079
attempts. Lidocaine is an alternative when ○ Severe hypoglycemia: dextrose 50% (0.5 g/ cells to maintain a normal blood pressure
and to allow quick lactate clearance.
kg IV/IO)
amiodarone is not available. ○ Pneumothorax: open-chest CPR ○ Respiratory optimization: support ventila-
VetBooks.ir IO) when CPR is prolonged (e.g., > 10 ○ Severe hemorrhage: resuscitative fluid tion and oxygenation (normal ETCO 2 and
○ Give sodium bicarbonate (1 mEq/kg IV/
minutes).
SpO 2 ) until the animal regains normal
therapy and blood transfusions
respiratory function.
• Defibrillation is the treatment of choice for
shockable rhythms (i.e., pVT or VF). Discontinuation of CPR: high-quality CPR ○ Targeted temperature management: main-
should be continued until one of the two
○ After a shockable rhythm is identified, occurs: tain hypothermia (33°C-37°C) if comatose,
defibrillate as early as possible while mini- • CPR is abandoned for futility or on owner’s and do not permit faster rewarming than
mally interrupting chest compressions. decision 0.5°C/h.
○ Apply ample amounts of defibrillator gel to • ROSC is achieved, recognized by ○ Consider administration of phenobarbital
the defibrillator electrodes (e.g., paddles). ○ Palpable femoral pulse to prevent seizures.
○ Charge the defibrillator to the Joules ○ Marked increase in ETCO 2 ○ Correct significant acid-base/electrolyte
appropriate for the animal’s size. abnormalities.
○ Interrupt chest compressions, and position Postprocedure ○ Provide analgesia and sedation as needed.
the paddles on either side of the chest over Postcardiac arrest (PCA) care is crucial for ○ Refer to a facility that can provide 24-hour Procedures and Techniques
the heart. a positive outcome. It encompasses two intensive care for further PCA care.
○ Apply ample pressure on the paddles to phases:
reduce impedance to current. • Prevention of re-arrest Alternatives and Their
○ Ensure that nobody is in contact with ○ Continue mechanical/manual ventilation Relative Merits
the animal (CLEAR!), and apply a single to achieve normoventilation (i.e., PaCO 2 CPR should be reserved for animals with
shock. = 35-40 mm Hg; ETCO 2 = 30-35 mm comorbidity levels that render return to an
○ Resume chest compressions for a full Hg) and oxygen supplementation for an acceptable quality of life possible. An advanced
2-minute cycle of CPR until next rhythm SpO 2 = 94%-98%. directive (e.g., resuscitation code) should be
analysis. ○ Start an epinephrine CRI at 0.1 mcg/ obtained from pet’s owner for all animals at
○ If VF/pVT persists, consider increasing kg/min and titrate to maintain a mean risk of CPA.
defibrillator dose by 50%. arterial blood pressure of 80 mm Hg
○ See electrical defibrillation (p. 1088). without inducing significant cardiac Pearls
• Identify and treat reversible causes of CPA. arrhythmias. • Do not delay initiation of CPR by using
○ Severe electrolyte abnormalities: hypoka- • Supportive care to minimize organ injury additional monitoring or testing. If in doubt,
lemia; hyperkalemia; hypocalcemia ○ Hemodynamic optimization: continue start CPR.
○ Severe metabolic acidosis: sodium bicar- vasopressors, inotropes, fluid therapy; • Quality of chest compressions is most impor-
bonate (1 mEq/kg IV/IO) consider possible transfusion of red blood tant for effective CPR. Training is essential!
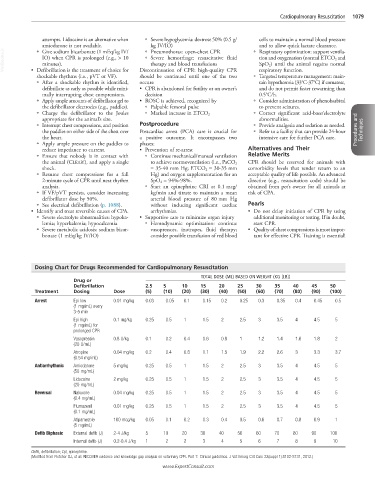
Dosing Chart for Drugs Recommended for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
TOTAL DOSE (ML) BASED ON WEIGHT (KG [LB])
Drug or
Defibrillation 2.5 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Treatment Dosing Dose (5) (10) (20) (30) (40) (50) (60) (70) (80) (90) (100)
Arrest Epi low 0.01 mg/kg 0.03 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
(1 mg/mL) every
3-5 min
Epi high 0.1 mg/kg 0.25 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
(1 mg/mL) for
prolonged CPR
Vasopressin 0.8 U/kg 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
(20 U/mL)
Atropine 0.04 mg/kg 0.2 0.4 0.8 1.1 1.5 1.9 2.2 2.6 3 3.3 3.7
(0.54 mg/mL)
Antiarrhythmic Amiodarone 5 mg/kg 0.25 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
(50 mg/mL)
Lidocaine 2 mg/kg 0.25 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
(20 mg/mL)
Reversal Naloxone 0.04 mg/kg 0.25 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
(0.4 mg/mL)
Flumazenil 0.01 mg/kg 0.25 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
(0.1 mg/mL)
Atipamezole 100 mcg/kg 0.05 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
(5 mg/mL)
Defib Biphasic External defib (J) 2-4 J/kg 5 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Internal defib (J) 0.2-0.4 J/kg 1 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Defib, defibrillation; Epi, epinephrine.
(Modified from Fletcher DJ, et al: RECOVER evidence and knowledge gap analysis on veterinary CPR. Part 7: Clinical guidelines. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 22(suppl 1):S102-S131, 2012.)
www.ExpertConsult.com