Page 2423 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2423
Ataxia 1201
(Continued from previous page)
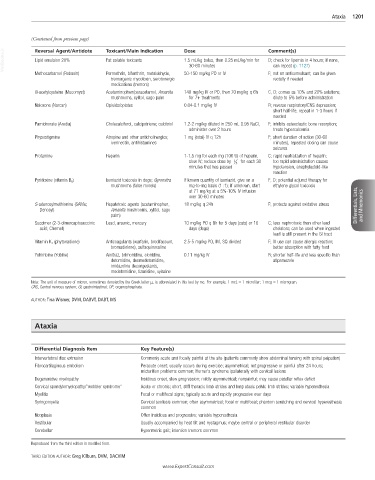
VetBooks.ir Reversal Agent/Antidote Toxicant/Main Indication Dose Comment(s)
D; check for lipemia in 4 hours; if none,
Lipid emulsion 20%
Fat soluble toxicants
1.5 mL/kg bolus, then 0.25 mL/kg/min for
can repeat (p. 1127)
30-60 minutes
Methocarbamol (Robaxin) Permethrin, bifenthrin, metaldehyde, 50-150 mg/kg PO or IV F; not an anticonvulsant; can be given
tremorgenic mycotoxin, serotonergic rectally if needed
medications (tremors)
N-acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) Acetaminophen/paracetamol, Amanita 140 mg/kg IV or PO, then 70 mg/kg q 6h C, D; comes as 10% and 20% solutions;
mushrooms, xylitol, sago palm for 7+ treatments dilute to 5% before administration
Naloxone (Narcan) Opioids/opiates 0.04-0.1 mg/kg IV R; reverse respiratory/CNS depression;
short half-life; repeat in 1-3 hours if
needed
Pamidronate (Aredia) Cholecalciferol, calcipotriene; calcitriol 1.2-2 mg/kg diluted in 250 mL 0.95 NaCl, F; inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption;
administer over 2 hours treats hypercalcemia
Physostigmine Atropine and other anticholinergics; 1 mg (total) IV q 12h F; short duration of action (30-60
ivermectin, antihistamines minutes), repeated dosing can cause
seizures
Protamine Heparin 1-1.5 mg for each mg (100 U) of heparin, C; rapid neutralization of heparin;
slow IV; reduce dose by 1 2 for each 30 too rapid administration causes
minutes that has passed hypotension, anaphylactoid-like
reaction
Pyridoxine (vitamin B 6) Isoniazid toxicosis in dogs; Gyromitra If known quantity of isoniazid, give on a F, D; potential adjunct therapy for
mushrooms (false morels) mg-to-mg basis (1 : 1); if unknown, start ethylene glycol toxicosis
at 71 mg/kg at a 5%-10% IV infusion
over 30-60 minutes
S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe; Hepatotoxic agents (acetaminophen, 18 mg/kg q 24h F; protects against oxidative stress Differentials, Lists, and Mnemonics
Denosyl) Amanita mushrooms, xylitol, sago
palm)
Succimer (2-3-dimercaptosuccinic Lead, arsenic, mercury 10 mg/kg PO q 8h for 5 days (cats) or 10 C; less nephrotoxic than other lead
acid; Chemet) days (dogs) chelators; can be used when ingested
lead is still present in the GI tract
Vitamin K 1 (phytonadione) Anticoagulants (warfarin, brodifacoum, 2.5-5 mg/kg PO, IM, SQ divided F; IV use can cause allergic reaction;
bromadiolone), sulfaquinoxaline better absorption with fatty food
Yohimbine (Yobine) Amitraz, brimonidine, clonidine, 0.11 mg/kg IV R; shorter half-life and less specific than
detomidine, dexmedetomidine, atipamezole
imidazoline decongestants,
medetomidine, tizanidine, xylazine
Note: The unit of measure of micron, sometimes denoted by the Greek letter μ, is abbreviated in this text by mc. For example, 1 mcL = 1 microliter; 1 mcg = 1 microgram.
CNS, Central nervous system; GI, gastrointestinal; OP, organophosphate.
AUTHOR: Tina Wismer, DVM, DABVT, DABT, MS
Ataxia
Differential Diagnosis Item Key Feature(s)
Intervertebral disc extrusion Commonly acute and focally painful at the site (patients commonly show abdominal tensing with spinal palpation)
Fibrocartilaginous embolism Peracute onset; usually occurs during exercise; asymmetrical; not progressive or painful after 24 hours;
micturition problems common; Horner’s syndrome ipsilaterally with cervical lesions
Degenerative myelopathy Insidious onset, slow progression; mildly asymmetrical; nonpainful; may cause patellar reflex deficit
Cervical spondylomyelopathy/“wobbler syndrome” Acute or chronic; short, stiff thoracic limb strides and long ataxic pelvic limb strides; variable hyperesthesia
Myelitis Focal or multifocal signs; typically acute and rapidly progressive over days
Syringomyelia Cervical scoliosis common; often asymmetrical; focal or multifocal; phantom scratching and cervical hyperesthesia
common
Neoplasia Often insidious and progressive; variable hyperesthesia
Vestibular Usually accompanied by heat tilt and nystagmus; maybe central or peripheral vestibular disorder
Cerebellar Hypermetric gait; intention tremors common
Reproduced from the third edition in modified form.
THIRD EDITION AUTHOR: Greg Kilburn, DVM, DACVIM
www.ExpertConsult.com