Page 2427 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2427
1202 Back Pain Bleeding Disorders: Primary versus Secondary
Back Pain
VetBooks.ir Differential Diagnoses Key Feature(s)
Intervertebral disc disease (IVDD) Variable degree of pain on palpation, often accompanied by proprioceptive deficits, ataxia, paresis, or paralysis
Acute noncompressive nucleus pulposus extrusion Acute or peracute onset; variable degrees of pain on palpation, proprioceptive deficits, ataxia, paresis, or paralysis
(ANNPE, Type III IVDD)
Vertebral fracture/luxation History or suspicion of trauma warrants early screening, spinal radiographs, but treat life-threatening injuries first;
neurologic status important for prognosis
Meningitis/meningomyelitis Often multifocal neurologic localization; may include signs of encephalitis
Discospondylitis/vertebral osteomyelitis Usually progressive over days to weeks; fever may accompany pain without radiographic changes early in the
course of disease
Neoplasia Most often chronic but may be acute presentation; primary or metastatic; spinal pain more common with vertebral
origin than meningeal or nerve parenchymal tumors
Ischemic myelopathy Acute but transient pain, resolving within hours; neurologic deficits may be asymmetrical; lower motor neuron
deficits associated with poorer prognosis
Orthopedic spinal pain Spondylosis deformans, articular facet degenerative joint disease, psoas muscle injury (lumbar)
Pain not localized to spinal column Aortic thromboembolism (cats), abdominal pain may mimic spinal pain, kidney pain, polyarthritis (multiple joint
effusion and pain), polymyopathy (diffuse muscle pain)
AUTHOR: Peter Moak, DVM
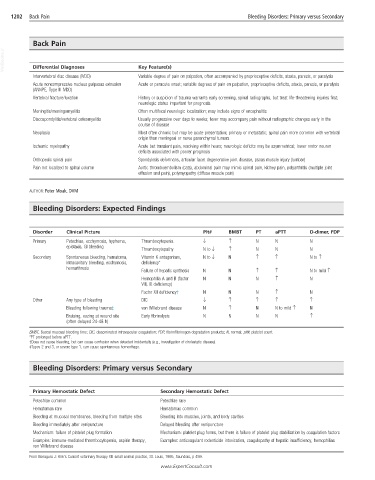
Bleeding Disorders: Expected Findings
Disorder Clinical Picture Plt# BMBT PT aPTT D-dimer, FDP
Primary Petechiae, ecchymosis, hyphema, Thrombocytopenia ↓ ↑ N N N
epistaxis, GI bleeding
Thrombocytopathy N to ↓ ↑ N N N
Secondary Spontaneous bleeding, hematoma, Vitamin K antagonism, N to ↓ N ↑ ↑ N to ↑
intracavitary bleeding, ecchymosis, deficiency*
hemarthrosis
Failure of hepatic synthesis N N ↑ ↑ N to mild ↑
Hemophilia A and B (factor N N N ↑ N
VIII, IX deficiency)
Factor XII deficiency† N N N ↑ N
Other Any type of bleeding DIC ↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
Bleeding following trauma‡ von Willebrand disease N ↑ N N to mild ↑ N
Bruising, oozing at wound site Early fibrinolysis N N N N ↑
(often delayed 24-48 h)
BMBT, Buccal mucosal bleeding time; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; FDP, fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products; N, normal; plt#, platelet count.
*PT prolonged before aPTT.
†Does not cause bleeding, but can cause confusion when detected incidentally (e.g., investigation of cholestatic disease).
‡Types 2 and 3, or severe type 1, can cause spontaneous hemorrhage.
Bleeding Disorders: Primary versus Secondary
Primary Hemostatic Defect Secondary Hemostatic Defect
Petechiae common Petechiae rare
Hematomas rare Hematomas common
Bleeding at mucosal membranes, bleeding from multiple sites Bleeding into muscles, joints, and body cavities
Bleeding immediately after venipuncture Delayed bleeding after venipuncture
Mechanism: failure of platelet plug formation Mechanism: platelet plug forms, but there is failure of platelet plug stabilization by coagulation factors
Examples: immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, aspirin therapy, Examples: anticoagulant rodenticide intoxication, coagulopathy of hepatic insufficiency, hemophilias
von Willebrand disease
From Bonagura J: Kirk’s Current veterinary therapy XII: small animal practice, St. Louis, 1995, Saunders, p 459.
www.ExpertConsult.com