Page 2424 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2424
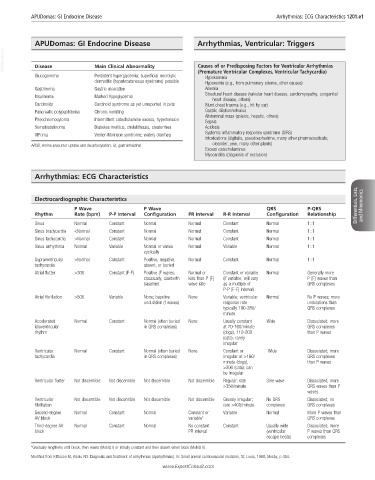
APUDomas: GI Endocrine Disease Arrhythmias: ECG Characteristics 1201.e1
APUDomas: GI Endocrine Disease Arrhythmias, Ventricular: Triggers
VetBooks.ir Disease Main Clinical Abnormality Causes of or Predisposing Factors for Ventricular Arrhythmias
Glucagonoma Persistent hyperglycemia; superficial necrolytic (Premature Ventricular Complexes, Ventricular Tachycardia)
Hypokalemia
dermatitis (hepatocutaneous syndrome) possible Hypoxemia (e.g., from pulmonary edema, other causes)
Gastrinoma Gastric ulceration Anemia
Structural heart disease (valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathy, congenital
Insulinoma Marked hypoglycemia heart disease, others)
Carcinoids Carcinoid syndrome as yet unreported in pets Blunt chest trauma (e.g., hit by car)
Pancreatic polypeptidoma Chronic vomiting Gastric dilation/volvulus
Abdominal mass (splenic, hepatic, others)
Pheochromocytoma Intermittent catecholamine excess, hypertension Sepsis
Somatostatinoma Diabetes mellitus, cholelithiasis, steatorrhea Acidosis
VIPoma Verner-Morrison syndrome; watery diarrhea Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
Intoxications (digitalis, pseudoephedrine, many other pharmaceuticals;
APUD, Amine precursor uptake and decarboxylation; GI, gastrointestinal. oleander, yew, many other plants)
Excess catecholamines
Myocarditis (diagnosis of exclusion)
Arrhythmias: ECG Characteristics
Electrocardiographic Characteristics
P Wave P Wave QRS P-QRS Differentials, Lists, and Mnemonics
Rhythm Rate (bpm) P-P Interval Configuration PR Interval R-R Interval Configuration Relationship
Sinus Normal Constant Normal Normal Constant Normal 1 : 1
Sinus bradycardia <Normal Constant Normal Normal Constant Normal 1 : 1
Sinus tachycardia >Normal Constant Normal Normal Constant Normal 1 : 1
Sinus arrhythmia Normal Variable Normal or varies Normal Variable Normal 1 : 1
cyclically
Supraventricular >Normal Constant Positive, negative, Normal Constant Normal 1 : 1
tachycardia absent, or buried
Atrial flutter >300 Constant (F-F) Positive (F waves; Normal or Constant or variable Normal Generally more
classically, sawtooth less than P [F] (if variable, will vary P [F] waves than
baseline) wave rate as a multiple of QRS complexes
P-P [F-F] interval)
Atrial fibrillation >500 Variable None; baseline None Variable; ventricular Normal No P waves; more
undulation (f waves) response rate undulations than
typically 100-280/ QRS complexes
minute
Accelerated Normal Constant Normal (often buried None Usually constant Wide Dissociated; more
idioventricular in QRS complexes) at 70-160/minute QRS complexes
rhythm (dogs), 110-200 than P waves
(cats); rarely
irregular
Ventricular Normal Constant Normal (often buried None Constant or Wide Dissociated; more
tachycardia in QRS complexes) irregular at >160/ QRS complexes
minute (dogs), than P waves
>200 (cats); can
be irregular
Ventricular flutter Not discernible Not discernible Not discernible Not discernible Regular; rate Sine wave Dissociated; more
>350/minute QRS waves than P
waves
Ventricular Not discernible Not discernible Not discernible Not discernible Grossly irregular; No QRS Dissociated; no
fibrillation rate >400/minute complexes QRS complexes
Second-degree Normal Constant Normal Constant or Variable Normal More P waves than
AV block variable* QRS complexes
Third-degree AV Normal Constant Normal No constant Constant Usually wide Dissociated; more
block PR interval (ventricular P waves than QRS
escape beats) complexes
*Gradually lengthens until block, then resets (Mobitz I) or initially constant and then absent when block (Mobitz II).
Modified from Kittleson M, Kienle RD: Diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias (dysrhythmias). In: Small animal cardiovascular medicine, St. Louis, 1998, Mosby, p 454.
www.ExpertConsult.com