Page 2518 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2518
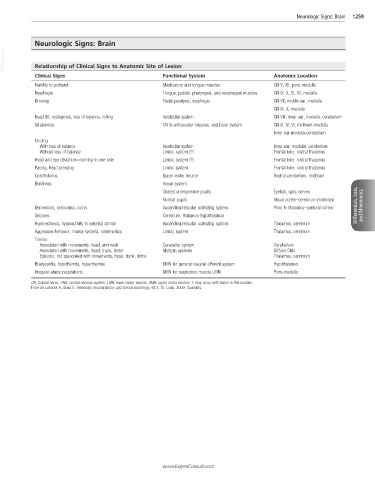
Neurologic Signs: Brain 1259
Neurologic Signs: Brain
VetBooks.ir Relationship of Clinical Signs to Anatomic Site of Lesion
Clinical Signs Functional System Anatomic Location
Inability to prehend Masticatory and tongue muscles CN V, XII, pons-medulla
Dysphagia Tongue, palatal, pharyngeal, and esophageal muscles CN IX, X, XI, XII, medulla
Drooling Facial paralysis, dysphagia CN VII, middle ear, medulla
CN IX, X, medulla
Head tilt, nystagmus, loss of balance, rolling Vestibular system CN VIII: inner ear, medulla, cerebellum
Strabismus CN to extraocular muscles, vestibular system CN III, IV, VI, midbrain-medulla
Inner ear-medulla-cerebellum
Circling
With loss of balance Vestibular system Inner ear, medulla, cerebellum
Without loss of balance Limbic system (?) Frontal lobe, rostral thalamus
Head and eye deviation—turning to one side Limbic system (?) Frontal lobe, rostral thalamus
Pacing, head pressing Limbic system Frontal lobe, rostral thalamus
Opisthotonos Upper motor neuron Rostral cerebellum, midbrain
Blindness Visual system
Dilated unresponsive pupils Eyeball, optic nerves
Normal pupils Visual cortex–cerebrum (midbrain)
Depression, semicoma, coma Ascending reticular activating system Pons to thalamus–cerebral cortex Differentials, Lists, and Mnemonics
Seizures Cerebrum, thalamus-hypothalamus
Hyperesthesia, hyperactivity to external stimuli Ascending reticular activating system Thalamus, cerebrum
Aggressive behavior, mania-hysteria, odontoprisis Limbic system Thalamus, cerebrum
Tremor
Associated with movements, head, and neck Cerebellar system Cerebellum
Associated with movements, head, trunk, limbs Multiple systems Diffuse CNS
Episodic, not associated with movements, head, trunk, limbs Thalamus, cerebrum
Bradycardia, hypothermia, hyperthermia UMN for general visceral efferent system Hypothalamus
Irregular-ataxic respirations UMN for respiratory muscle LMN Pons-medulla
CN, Cranial nerve; CNS, central nervous system; LMN, lower motor neuron; UMN, upper motor neuron; ?, may occur with lesion in this location.
From de Lahunta A, Glass E: Veterinary neuroanatomy and clinical neurology, ed 3, St. Louis, 2009, Saunders.
www.ExpertConsult.com