Page 760 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 760
Fractures of the Femur 359
• When a comminuted fracture is being
repaired, all bone fragments should be retained
VetBooks.ir • Delayed unions and nonunions are often Diseases and Disorders
unless they are contaminated; removing them
increases the likelihood of nonunion.
associated with poor decision making or
technical failures on the part of the intervening
surgeon. Patient factors and owner compliance
are less common reasons for nonunions.
Technician Tips
Fracture healing can be difficult to assess due
to superimposition of metal implants. Oblique
views can be a helpful addition to the normal
orthogonal views.
Client Education
• Postoperative care instructions require com-
munication (spoken and written) between
the surgeon(s) and owner. There needs to be
a clear understanding of expectations and
follow-up requirements.
• Clients need to understand they are an
important part of this process from the begin-
ning, and that compliance with postoperative
instructions for exercise restriction, follow-up
exams, appropriate physical therapy, and
consistent administration of all medications
is critical to achieving a successful outcome.
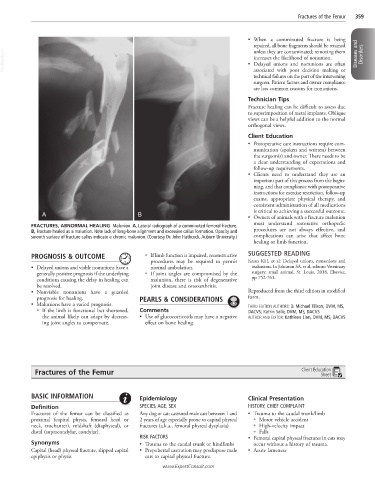
A B • Owners of animals with a fracture malunion
FRACTURES, ABNORMAL HEALING Malunion. A, Lateral radiograph of a comminuted femoral fracture. must understand restorative orthopedic
B, Fracture healed as a malunion. Note lack of long-bone alignment and excessive callus formation. Opacity and procedures are not always effective, and
smooth surface of fracture callus indicate a chronic malunion. (Courtesy Dr. John Hathcock, Auburn University.) complications can arise that affect bone
healing or limb function.
PROGNOSIS & OUTCOME ○ If limb function is impaired, reconstructive SUGGESTED READING
procedures may be required to permit Kraus KH, et al: Delayed unions, nonunions and
• Delayed unions and viable nonunions have a normal ambulation. malunions. In Johnston SA, et al, editors: Veterinary
generally positive prognosis if the underlying ○ If joint angles are compromised by the surgery: small animal, St. Louis, 2018, Elsevier,
conditions causing the delay in healing can malunion, there is risk of degenerative pp 752-761.
be resolved. joint disease and osteoarthritis.
• Nonviable nonunions have a guarded Reproduced from the third edition in modified
prognosis for healing. PEARLS & CONSIDERATIONS form.
• Malunions have a varied prognosis. THIRD EDITION AUTHORS: D. Michael Tillson, DVM, MS,
○ If the limb is functional but shortened, Comments DACVS; Katrin Saile, DVM, MS, DACVS
the animal likely can adapt by decreas- • Use of glucocorticoids may have a negative AUTHOR AND EDITOR: Kathleen Linn, DVM, MS, DACVS
ing joint angles to compensate. effect on bone healing.
Fractures of the Femur Client Education
Sheet
BASIC INFORMATION Epidemiology Clinical Presentation
Definition SPECIES, AGE, SEX HISTORY, CHIEF COMPLAINT
Fractures of the femur can be classified as Any dog or cat; castrated male cats between 1 and • Trauma to the caudal trunk/limb
proximal (capital physis, femoral head or 2 years of age especially prone to capital physeal ○ Motor vehicle accident
neck, trochanter), midshaft (diaphyseal), or fractures (a.k.a., femoral physeal dysplasia) ○ High-velocity impact
distal (supracondylar, condylar). ○ Falls
RISK FACTORS • Femoral capital physeal fractures in cats may
Synonyms • Trauma to the caudal trunk or hindlimbs occur without a history of trauma.
Capital (head) physeal fracture, slipped capital • Prepubertal castration may predispose male • Acute lameness
epiphysis or physis cats to capital physeal fracture.
www.ExpertConsult.com