Page 476 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 476
448 PART III Digestive System Disorders
protruding from the mouth. Papillomatosis and fibromatous cytologic or histopathologic analysis, although papillomato-
periodontal hyperplasia are benign growths that may cause sis and melanomas may be strongly suspected based upon
VetBooks.ir discomfort when eating and occasionally cause bleeding, their gross appearance. The preferred diagnostic approach in
a dog with a mass of the oral cavity is to image the area (e.g.,
mild halitosis, or tissue protrusion from the mouth. The
biologic behaviors of the different tumors are presented in
biopsy is necessary to avoid misdiagnosis that often occurs
Table 29.1. CT) and perform a relatively deep incisional biopsy. A deep
if only the superficial, ulcerated, necrotic surface is obtained.
Diagnosis If malignancy is possible, thoracic radiographs or CT should
A thorough examination of the oral cavity (which may be obtained to evaluate for metastases (uncommon but a
require that the animal be under anesthesia) usually reveals very poor prognostic sign if present). Fine-needle aspiration
a mass involving the gingiva, although the tonsillar area, of regional lymph nodes, even if they appear normal, is indi-
hard palate, and tongue may be affected. Diagnosis requires cated to detect metastases. Melanomas may be amelanotic
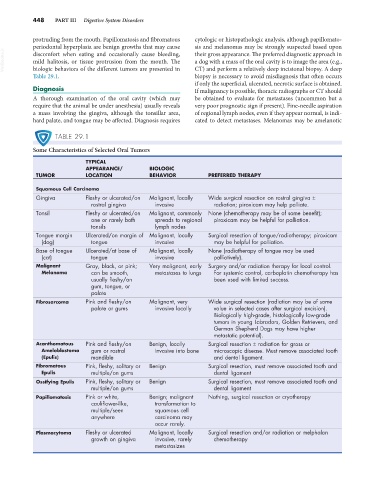
TABLE 29.1
Some Characteristics of Selected Oral Tumors
TYPICAL
APPEARANCE/ BIOLOGIC
TUMOR LOCATION BEHAVIOR PREFERRED THERAPY
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Gingiva Fleshy or ulcerated/on Malignant, locally Wide surgical resection on rostral gingiva ±
rostral gingiva invasive radiation; piroxicam may help palliate.
Tonsil Fleshy or ulcerated/on Malignant, commonly None (chemotherapy may be of some benefit);
one or rarely both spreads to regional piroxicam may be helpful for palliation.
tonsils lymph nodes
Tongue margin Ulcerated/on margin of Malignant, locally Surgical resection of tongue/radiotherapy; piroxicam
(dog) tongue invasive may be helpful for palliation.
Base of tongue Ulcerated/at base of Malignant, locally None (radiotherapy of tongue may be used
(cat) tongue invasive palliatively).
Malignant Gray, black, or pink; Very malignant, early Surgery and/or radiation therapy for local control.
Melanoma can be smooth, metastases to lungs For systemic control, carboplatin chemotherapy has
usually fleshy/on been used with limited success.
gum, tongue, or
palate
Fibrosarcoma Pink and fleshy/on Malignant, very Wide surgical resection (radiation may be of some
palate or gums invasive locally value in selected cases after surgical excision).
Biologically high-grade, histologically low-grade
tumors in young Labradors, Golden Retrievers, and
German Shepherd Dogs may have higher
metastatic potential).
Acanthomatous Pink and fleshy/on Benign, locally Surgical resection ± radiation for gross or
Ameloblastoma gum or rostral invasive into bone microscopic disease. Must remove associated tooth
(Epulis) mandible and dental ligament.
Fibromatous Pink, fleshy, solitary or Benign Surgical resection, must remove associated tooth and
Epulis multiple/on gums dental ligament
Ossifying Epulis Pink, fleshy, solitary or Benign Surgical resection, must remove associated tooth and
multiple/on gums dental ligament
Papillomatosis Pink or white, Benign; malignant Nothing, surgical resection or cryotherapy
cauliflower-like, transformation to
multiple/seen squamous cell
anywhere carcinoma may
occur rarely.
Plasmacytoma Fleshy or ulcerated Malignant, locally Surgical resection and/or radiation or melphalan
growth on gingiva invasive, rarely chemotherapy
metastasizes