Page 1260 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1260
cause myositis, and anti-myocardial antibodies may provoke
VetBooks.ir myocarditis or endocarditis. Antibodies to skin basement
membrane cause a dermatitis characterized by changes in
epidermal thickness, focal mononuclear cell infiltration, collagen
degeneration, and immunoglobulin deposits at the
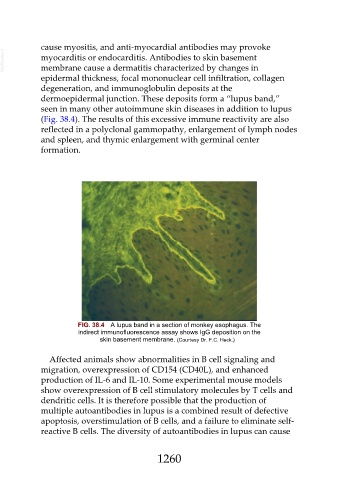
dermoepidermal junction. These deposits form a “lupus band,”
seen in many other autoimmune skin diseases in addition to lupus
(Fig. 38.4). The results of this excessive immune reactivity are also
reflected in a polyclonal gammopathy, enlargement of lymph nodes
and spleen, and thymic enlargement with germinal center
formation.
FIG. 38.4 A lupus band in a section of monkey esophagus. The
indirect immunofluorescence assay shows IgG deposition on the
skin basement membrane. (Courtesy Dr. F.C. Heck.)
Affected animals show abnormalities in B cell signaling and
migration, overexpression of CD154 (CD40L), and enhanced
production of IL-6 and IL-10. Some experimental mouse models
show overexpression of B cell stimulatory molecules by T cells and
dendritic cells. It is therefore possible that the production of
multiple autoantibodies in lupus is a combined result of defective
apoptosis, overstimulation of B cells, and a failure to eliminate self-
reactive B cells. The diversity of autoantibodies in lupus can cause
1260