Page 310 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 310
Haematology 279
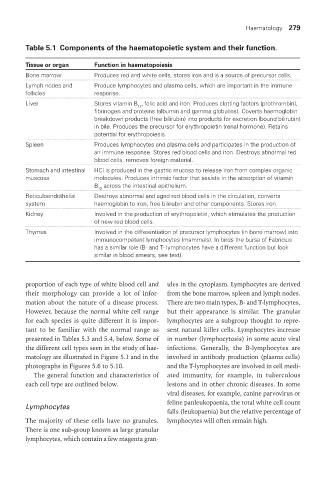
Table 5.1 Components of the haematopoietic system and their function.
Tissue or organ Function in haematopoiesis
Bone marrow Produces red and white cells, stores iron and is a source of precursor cells.
Lymph nodes and Produce lymphocytes and plasma cells, which are important in the immune
follicles response.
Liver Stores vitamin B , folic acid and iron. Produces clotting factors (prothrombin),
12
fibrinogen and proteins (albumin and gamma globulins). Coverts haemoglobin
breakdown products (free bilirubin) into products for excretion (bound bilirubin)
in bile. Produces the precursor for erythropoietin (renal hormone). Retains
potential for erythropoiesis.
Spleen Produces lymphocytes and plasma cells and participates in the production of
an immune response. Stores red blood cells and iron. Destroys abnormal red
blood cells, removes foreign material.
Stomach and intestinal HCl is produced in the gastric mucosa to release iron from complex organic
muscosa molecules. Produces intrinsic factor that assists in the absorption of vitamin
B across the intestinal epithelium.
12
Reticuloendothelial Destroys abnormal and aged red blood cells in the circulation, converts
system haemoglobin to iron, free bilirubin and other components. Stores iron.
Kidney Involved in the production of erythropoietin, which stimulates the production
of new red blood cells.
Thymus Involved in the differentiation of precursor lymphocytes (in bone marrow) into
immunocompetent lymphocytes (mammals). In birds the bursa of Fabricius
has a similar role (B- and T- lymphocytes have a different function but look
similar in blood smears, see text).
proportion of each type of white blood cell and ules in the cytoplasm. Lymphocytes are derived
their morphology can provide a lot of infor- from the bone marrow, spleen and lymph nodes.
mation about the nature of a disease process. There are two main types, B- and T-lymphocytes,
However, because the normal white cell range but their appearance is similar. The granular
for each species is quite different it is impor- lymphocytes are a subgroup thought to repre-
tant to be familiar with the normal range as sent natural killer cells. Lymphocytes increase
presented in Tables 5.3 and 5.4, below. Some of in number (lymphocytosis) in some acute viral
the different cell types seen in the study of hae- infections. Generally, the B-lymphocytes are
matology are illustrated in Figure 5.1 and in the involved in antibody production (plasma cells)
photographs in Figures 5.6 to 5.10. and the T-lymphocytes are involved in cell medi-
The general function and characteristics of ated immunity, for example, in tuberculous
each cell type are outlined below. lesions and in other chronic diseases. In some
viral diseases, for example, canine parvovirus or
feline panleukopaenia, the total white cell count
Lymphocytes
falls (leukopaenia) but the relative percentage of
The majority of these cells have no granules. lymphocytes will often remain high.
There is one sub-group known as large granular
lymphocytes, which contain a few magenta gran-
Vet Lab.indb 279 26/03/2019 10:25