Page 368 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 368
Clinical chemistry 337
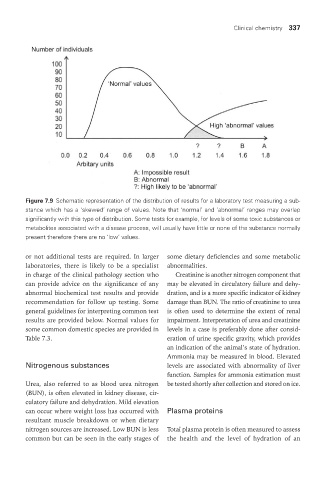
Figure 7.9 Schematic representation of the distribution of results for a laboratory test measuring a sub-
stance which has a ‘skewed’ range of values. Note that ‘normal’ and ‘abnormal’ ranges may overlap
significantly with this type of distribution. Some tests for example, for levels of some toxic substances or
metabolites associated with a disease process, will usually have little or none of the substance normally
present therefore there are no ‘low’ values.
or not additional tests are required. In larger some dietary deficiencies and some metabolic
laboratories, there is likely to be a specialist abnormalities.
in charge of the clinical pathology section who Creatinine is another nitrogen component that
can provide advice on the significance of any may be elevated in circulatory failure and dehy-
abnormal biochemical test results and provide dration, and is a more specific indicator of kidney
recommendation for follow up testing. Some damage than BUN. The ratio of creatinine to urea
general guidelines for interpreting common test is often used to determine the extent of renal
results are provided below. Normal values for impairment. Interpretation of urea and creatinine
some common domestic species are provided in levels in a case is preferably done after consid-
Table 7.3. eration of urine specific gravity, which provides
an indication of the animal’s state of hydration.
Ammonia may be measured in blood. Elevated
nitrogenous substances levels are associated with abnormality of liver
function. Samples for ammonia estimation must
Urea, also referred to as blood urea nitrogen be tested shortly after collection and stored on ice.
(BUN), is often elevated in kidney disease, cir-
culatory failure and dehydration. Mild elevation
can occur where weight loss has occurred with Plasma proteins
resultant muscle breakdown or when dietary
nitrogen sources are increased. Low BUN is less Total plasma protein is often measured to assess
common but can be seen in the early stages of the health and the level of hydration of an
Vet Lab.indb 337 26/03/2019 10:26