Page 489 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 489
Lameness of the Distal Limb 455
necessary to avoid confusing the lines from the lateral
sulci of the frog that cross the navicular region with a
VetBooks.ir navicular bone, it is usually not a fracture. When in
fracture. If the line extends beyond (above or below) the
doubt, it is best to retake the radiograph at a slightly
different angle. Complete simple fractures are typically
located in the sagittal plane medial or lateral to the mid-
line (parasagittal). 37,95 Most complete fractures are best
identified on the skyline or 60° oblique views of the
navicular bone and should be present on multiple views
(Figures 4.18 and 4.19). The fracture line should begin
and end at the edges of the navicular bone and is usually
easily visible, especially in chronic fractures. Navicular
bone fractures need to be differentiated from congenital
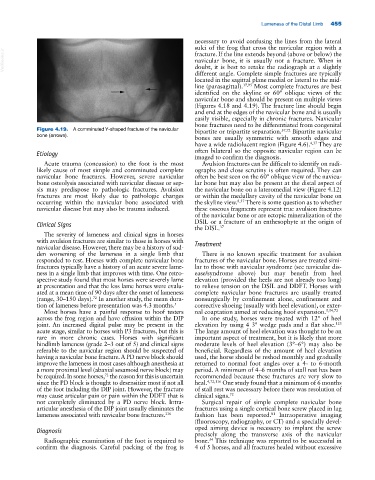
Figure 4.19. A comminuted Y‐shaped fracture of the navicular bipartite or tripartite separation. 37,72 Bipartite navicular
bone (arrows).
bones are usually symmetric with smooth edges and
have a wide radiolucent region (Figure 4.6). 4,37 They are
Etiology often bilateral so the opposite navicular region can be
imaged to confirm the diagnosis.
Acute trauma (concussion) to the foot is the most Avulsion fractures can be difficult to identify on radi-
likely cause of most simple and comminuted complete ographs and close scrutiny is often required. They can
navicular bone fractures. However, severe navicular often be best seen on the 60° oblique view of the navicu-
bone osteolysis associated with navicular disease or sep- lar bone but may also be present at the distal aspect of
sis may predispose to pathologic fractures. Avulsion the navicular bone on a lateromedial view (Figure 4.12)
fractures are most likely due to pathologic changes or within the medullary cavity of the navicular bone on
occurring within the navicular bone associated with the skyline view. 8,37 There is some question as to whether
navicular disease but may also be trauma induced. these osseous fragments represent true avulsion fractures
of the navicular bone or are ectopic mineralization of the
DSIL or a fracture of an enthesophyte at the origin of
Clinical Signs
the DISL. 37
The severity of lameness and clinical signs in horses
with avulsion fractures are similar to those in horses with Treatment
navicular disease. However, there may be a history of sud-
den worsening of the lameness in a single limb that There is no known specific treatment for avulsion
responded to rest. Horses with complete navicular bone fractures of the navicular bone. Horses are treated simi-
fractures typically have a history of an acute severe lame- lar to those with navicular syndrome (see navicular dis-
ness in a single limb that improves with time. One retro- ease/syndrome above) but may benefit from heel
spective study found that most horses were severely lame elevation (provided the heels are not already too long)
at presentation and that the less lame horses were evalu- to relieve tension on the DSIL and DDFT. Horses with
ated at a mean time of 90 days after the onset of lameness complete navicular bone fractures are usually treated
(range, 30–150 days). In another study, the mean dura- nonsurgically by confinement alone, confinement and
72
tion of lameness before presentation was 4.3 months. 5 corrective shoeing (usually with heel elevation), or exter-
Most horses have a painful response to hoof testers nal coaptation aimed at reducing hoof expansion. 5,54,72
across the frog region and have effusion within the DIP In one study, horses were treated with 12° of heel
joint. An increased digital pulse may be present in the elevation by using 4 3° wedge pads and a flat shoe.
123
acute stage, similar to horses with P3 fractures, but this is The large amount of heel elevation was thought to be an
rare in more chronic cases. Horses with significant important aspect of treatment, but it is likely that more
hindlimb lameness (grade 2–3 out of 5) and clinical signs moderate levels of heel elevation (3°–6°) may also be
referable to the navicular region should be suspected of beneficial. Regardless of the amount of heel elevation
having a navicular bone fracture. A PD nerve block should used, the horse should be reshod monthly and gradually
improve the lameness in most cases although anesthesia at returned to normal foot angles over a 4‐ to 6‐month
a more proximal level (abaxial sesamoid nerve block) may period. A minimum of 4–6 months of stall rest has been
be required. In some horses, the reason for this is uncertain recommended because these fractures are very slow to
72
since the PD block is thought to desensitize most if not all heal. 4,72,116 One study found that a minimum of 6 months
of the foot including the DIP joint. However, the fracture of stall rest was necessary before there was resolution of
may cause articular pain or pain within the DDFT that is clinical signs. 72
not completely eliminated by a PD nerve block. Intra‐ Surgical repair of simple complete navicular bone
articular anesthesia of the DIP joint usually eliminates the fractures using a single cortical bone screw placed in lag
lameness associated with navicular bone fractures. 116 fashion has been reported. Intraoperative imaging
81
(fluoroscopy, radiography, or CT) and a specially devel-
oped aiming device is necessary to implant the screw
Diagnosis
precisely along the transverse axis of the navicular
Radiographic examination of the foot is required to bone. This technique was reported to be successful in
54
confirm the diagnosis. Careful packing of the frog is 4 of 5 horses, and all fractures healed without excessive