Page 839 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 839
Principles of Musculoskeletal Disease 805
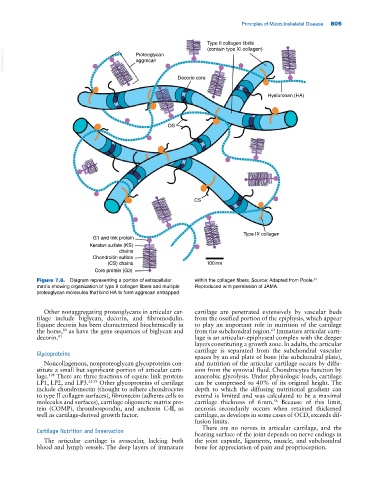
Type II collagen fibrils
(contain type XI collagen)
VetBooks.ir Proteoglycan
aggrecan
Decorin core
Hyaluronan (HA)
DS
CS
Type IX collagen
G1 and link protein
Keratan sulfate (KS)
chains
Chondroitin sulfate
(CS) chains 100nm
Core protein (G3)
Figure 7.6. Diagram representing a portion of extracellular within the collagen fibers. Source: Adapted from Poole.
81
matrix showing organization of type II collagen fibers and multiple Reproduced with permission of JAMA.
proteoglycan molecules that bind HA to form aggrecan entrapped
Other nonaggregating proteoglycans in articular car cartilage are penetrated extensively by vascular buds
tilage include biglycan, decorin, and fibromodulin. from the ossified portion of the epiphysis, which appear
Equine decorin has been characterized biochemically in to play an important role in nutrition of the cartilage
the horse, as have the gene sequences of biglycan and from the subchondral region. Immature articular carti
63
80
decorin. 81 lage is an articular–epiphyseal complex with the deeper
layers constituting a growth zone. In adults, the articular
cartilage is separated from the subchondral vascular
Glycoproteins spaces by an end plate of bone (the subchondral plate),
Noncollagenous, nonproteoglycan glycoproteins con and nutrition of the articular cartilage occurs by diffu
stitute a small but significant portion of articular carti sion from the synovial fluid. Chondrocytes function by
lage. There are three fractions of equine link protein: anaerobic glycolysis. Under physiologic loads, cartilage
108
LP1, LP2, and LP3. 23,79 Other glycoproteins of cartilage can be compressed to 40% of its original height. The
include chondronectin (thought to adhere chondrocytes depth to which the diffusing nutritional gradient can
to type II collagen surfaces), fibronectin (adheres cells to extend is limited and was calculated to be a maximal
molecules and surfaces), cartilage oligomeric matrix pro cartilage thickness of 6 mm. Because of this limit,
56
tein (COMP), thrombospondin, and anchorin C‐II, as necrosis secondarily occurs when retained thickened
well as cartilage‐derived growth factor. cartilage, as develops in some cases of OCD, exceeds dif
fusion limits.
There are no nerves in articular cartilage, and the
Cartilage Nutrition and Innervation bearing surface of the joint depends on nerve endings in
The articular cartilage is avascular, lacking both the joint capsule, ligaments, muscle, and subchondral
blood and lymph vessels. The deep layers of immature bone for appreciation of pain and proprioception.