Page 646 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 646
Respir atory system: 3.2 Surgical conditions of the respir atory tr act 621
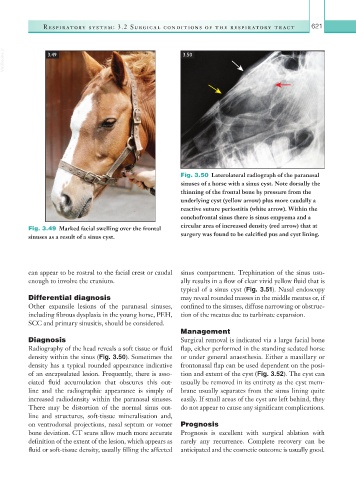
VetBooks.ir 3.49 3.50
Fig. 3.50 Laterolateral radiograph of the paranasal
sinuses of a horse with a sinus cyst. Note dorsally the
thinning of the frontal bone by pressure from the
underlying cyst (yellow arrow) plus more caudally a
reactive suture periostitis (white arrow). Within the
conchofrontal sinus there is sinus empyema and a
Fig. 3.49 Marked facial swelling over the frontal circular area of increased density (red arrow) that at
sinuses as a result of a sinus cyst. surgery was found to be calcified pus and cyst lining.
can appear to be rostral to the facial crest or caudal sinus compartment. Trephination of the sinus usu-
enough to involve the cranium. ally results in a flow of clear vivid yellow fluid that is
typical of a sinus cyst (Fig. 3.51). Nasal endoscopy
Differential diagnosis may reveal rounded masses in the middle meatus or, if
Other expansile lesions of the paranasal sinuses, confined to the sinuses, diffuse narrowing or obstruc-
including fibrous dysplasia in the young horse, PEH, tion of the meatus due to turbinate expansion.
SCC and primary sinusitis, should be considered.
Management
Diagnosis Surgical removal is indicated via a large facial bone
Radiography of the head reveals a soft tissue or fluid flap, either performed in the standing sedated horse
density within the sinus (Fig. 3.50). Sometimes the or under general anaesthesia. Either a maxillary or
density has a typical rounded appearance indicative frontonasal flap can be used dependent on the posi-
of an encapsulated lesion. Frequently, there is asso- tion and extent of the cyst (Fig. 3.52). The cyst can
ciated fluid accumulation that obscures this out- usually be removed in its entirety as the cyst mem-
line and the radiographic appearance is simply of brane usually separates from the sinus lining quite
increased radiodensity within the paranasal sinuses. easily. If small areas of the cyst are left behind, they
There may be distortion of the normal sinus out- do not appear to cause any significant complications.
line and structures, soft-tissue mineralisation and,
on ventrodorsal projections, nasal septum or vomer Prognosis
bone deviation. CT scans allow much more accurate Prognosis is excellent with surgical ablation with
definition of the extent of the lesion, which appears as rarely any recurrence. Complete recovery can be
fluid or soft-tissue density, usually filling the affected anticipated and the cosmetic outcome is usually good.