Page 227 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 227
212 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
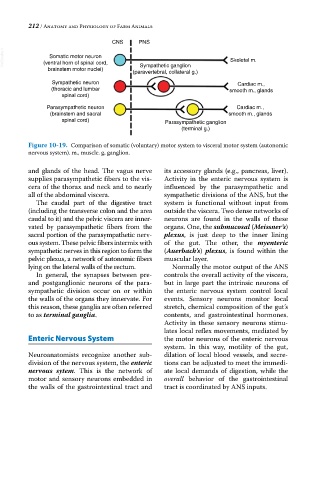
CNS PNS
VetBooks.ir (ventral horn of spinal cord, Skeletal m.
Somatic motor neuron
brainstem motor nuclei) Sympathetic ganglion
(paravertebral, collateral g.)
Sympathetic neuron Cardiac m.,
(thoracic and lumbar smooth m., glands
spinal cord)
Parasympathetic neuron Cardiac m.,
(brainstem and sacral smooth m., glands
spinal cord) Parasympathetic ganglion
(terminal g.)
Figure 10-19. Comparison of somatic (voluntary) motor system to visceral motor system (autonomic
nervous system). m., muscle. g, ganglion.
and glands of the head. The vagus nerve its accessory glands (e.g., pancreas, liver).
supplies parasympathetic fibers to the vis- Activity in the enteric nervous system is
cera of the thorax and neck and to nearly influenced by the parasympathetic and
all of the abdominal viscera. sympathetic divisions of the ANS, but the
The caudal part of the digestive tract system is functional without input from
(including the transverse colon and the area outside the viscera. Two dense networks of
caudal to it) and the pelvic viscera are inner- neurons are found in the walls of these
vated by parasympathetic fibers from the organs. One, the submucosal (Meissner’s)
sacral portion of the parasympathetic nerv- plexus, is just deep to the inner lining
ous system. These pelvic fibers intermix with of the gut. The other, the myenteric
sympathetic nerves in this region to form the (Auerbach’s) plexus, is found within the
pelvic plexus, a network of autonomic fibers muscular layer.
lying on the lateral walls of the rectum. Normally the motor output of the ANS
In general, the synapses between pre‐ controls the overall activity of the viscera,
and postganglionic neurons of the para- but in large part the intrinsic neurons of
sympathetic division occur on or within the enteric nervous system control local
the walls of the organs they innervate. For events. Sensory neurons monitor local
this reason, these ganglia are often referred stretch, chemical composition of the gut’s
to as terminal ganglia. contents, and gastrointestinal hormones.
Activity in these sensory neurons stimu-
lates local reflex movements, mediated by
Enteric Nervous System the motor neurons of the enteric nervous
system. In this way, motility of the gut,
Neuroanatomists recognize another sub- dilation of local blood vessels, and secre-
division of the nervous system, the enteric tions can be adjusted to meet the immedi-
nervous sytem. This is the network of ate local demands of digestion, while the
motor and sensory neurons embedded in overall behavior of the gastrointestinal
the walls of the gastrointestinal tract and tract is coordinated by ANS inputs.