Page 229 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 229
214 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
effects of parasympathetic and sympa (the action potential) down to the teloden
thetic input on the organs they target.
drion where it initiates the steps leading to
VetBooks.ir • Identify the neurotransmitters and recep synaptic transmission of information to
target cells (Fig. 11‐1).
tors found at the autonomic ganglion
synapse, between sympathetic neurons
and their targets, and between parasym
pathetic neurons and their targets. Physiology of the Nerve Impulse
• Explain how axonal regeneration in the
PNS differs from that in the CNS. Nerves rapidly transmit information from
one body site to another via action poten
tials propagated along the axons of neurons
Functional Regions of the Neuron within the nerves. The genesis of a resting
membrane potential and the development
Recall from Figures 10‐2 and 10‐3 that of action potentials and their propagation
neurons have cell bodies with processes are described in detail in Chapter 2 and are
extending from them. Of these cellular only briefly reviewed here.
extensions, one is an axon, and all others The specific resting membrane potential
are considered dendrites. With the excep of neurons depends on: (1) the electrogenic
tion of the pseudounipolar neurons in Na –K –ATPase, or Na –K , pump, which
+
+
+
+
the peripheral nervous system (PNS), the moves potassium ions (K ) into and sodium
+
dendrites and cell body represent the ions (Na ) out of the cell; (2) nongated
+
receptive zone of the neuron, where it (“leak”) potassium channels in the cell
receives information from other neurons. membrane; and (3) the presence of large,
The axon is the conducting zone of the negatively charged molecules in the cell’s
neuron, where the specialized ion channels interior (Fig. 11‐2). The net effect of these
in the axon’s membrane permit the rapid forces is that the inside of the cell is more
conduction of a wave of depolarization negative than its exterior.
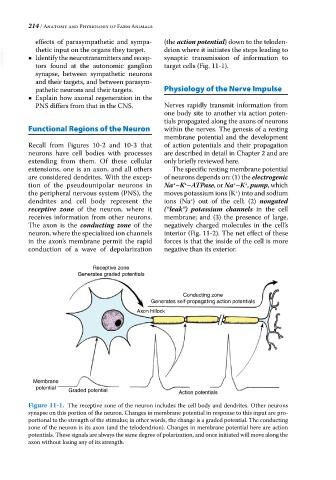
Receptive zone
Generates graded potentials
Conducting zone
Generates self-propagating action potentials
Axon hillock
Membrane
potential
Graded potential Action potentials
Figure 11-1. The receptive zone of the neuron includes the cell body and dendrites. Other neurons
synapse on this portion of the neuron. Changes in membrane potential in response to this input are pro
portional to the strength of the stimulus; in other words, the change is a graded potential. The conducting
zone of the neuron is its axon (and the telodendrion). Changes in membrane potential here are action
potentials. These signals are always the same degree of polarization, and once initiated will move along the
axon without losing any of its strength.