Page 333 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 333
318 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
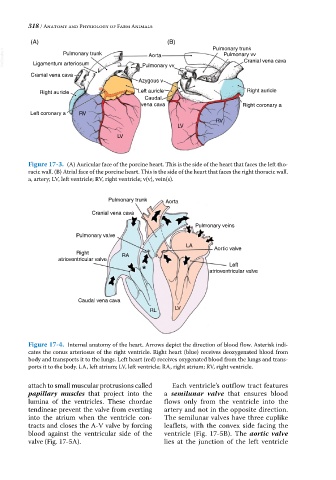
(A) (B)
Pulmonary trunk
VetBooks.ir Ligamentum arteriosum Pulmonary vv Pulmonary vv
Pulmonary trunk
Aorta
Cranial vena cava
Cranial vena cava
Azygous v
Right auricle Left auricle Right auricle
Caudal
vena cava Right coronary a
Left coronary a RV
RV
LV
LV
Figure 17-3. (A) Auricular face of the porcine heart. This is the side of the heart that faces the left tho-
racic wall. (B) Atrial face of the porcine heart. This is the side of the heart that faces the right thoracic wall.
a, artery; LV, left ventricle; RV, right ventricle; v(v), vein(s).
Pulmonary trunk Aorta
Cranial vena cava
Pulmonary veins
Pulmonary valve
LA Aortic valve
Right RA
atrioventricular valve
Left
atrioventricular valve
Caudal vena cava
RL LV
Figure 17-4. Internal anatomy of the heart. Arrows depict the direction of blood flow. Asterisk indi-
cates the conus arteriosus of the right ventricle. Right heart (blue) receives deoxygenated blood from
body and transports it to the lungs. Left heart (red) receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and trans-
ports it to the body. LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle.
attach to small muscular protrusions called Each ventricle’s outflow tract features
papillary muscles that project into the a semilunar valve that ensures blood
lumina of the ventricles. These chordae flows only from the ventricle into the
tendineae prevent the valve from everting artery and not in the opposite direction.
into the atrium when the ventricle con- The semilunar valves have three cuplike
tracts and closes the A‐V valve by forcing leaflets, with the convex side facing the
blood against the ventricular side of the ventricle (Fig. 17‐5B). The aortic valve
valve (Fig. 17‐5A). lies at the junction of the left ventricle