Page 328 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 328
Body Defenses and the Immune System / 313
trabeculae, penetrate into the interior of the The spleen is also an important site where
senescent (old and worn‐out) red blood
organ, forming a connective tissue frame-
VetBooks.ir work (Fig. 16‐5). The shape of the spleen var- cells are removed from the circulation,
broken down, and their iron stored. These
ies considerably from one species to another,
being long and thin in the pig, oblong in blood‐related functions are associated
cattle, and sickle‐shaped in the horse. with the red pulp of the splenic paren-
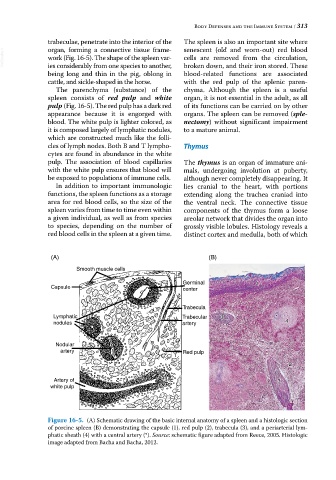
The parenchyma (substance) of the chyma. Although the spleen is a useful
spleen consists of red pulp and white organ, it is not essential in the adult, as all
pulp (Fig. 16‐5). The red pulp has a dark red of its functions can be carried on by other
appearance because it is engorged with organs. The spleen can be removed (sple-
blood. The white pulp is lighter colored, as nectomy) without significant impairment
it is composed largely of lymphatic nodules, to a mature animal.
which are constructed much like the folli-
cles of lymph nodes. Both B and T lympho- Thymus
cytes are found in abundance in the white
pulp. The association of blood capillaries The thymus is an organ of immature ani-
with the white pulp ensures that blood will mals, undergoing involution at puberty,
be exposed to populations of immune cells. although never completely disappearing. It
In addition to important immunologic lies cranial to the heart, with portions
functions, the spleen functions as a storage extending along the trachea craniad into
area for red blood cells, so the size of the the ventral neck. The connective tissue
spleen varies from time to time even within components of the thymus form a loose
a given individual, as well as from species areolar network that divides the organ into
to species, depending on the number of grossly visible lobules. Histology reveals a
red blood cells in the spleen at a given time. distinct cortex and medulla, both of which
(A) (B)
Smooth muscle cells
Germinal 1
Capsule center
Trabecula
Lymphatic Trabecular 3 *
nodules artery 4
Nodular
artery Red pulp
2
Artery of 3
white pulp
Figure 16-5. (A) Schematic drawing of the basic internal anatomy of a spleen and a histologic section
of porcine spleen (B) demonstrating the capsule (1), red pulp (2), trabecula (3), and a periarterial lym-
phatic sheath (4) with a central artery (*). Source: schematic figure adapted from Reece, 2005. Histologic
image adapted from Bacha and Bacha, 2012.