Page 234 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 234
202 Section 3 Cardiovascular Disease
VetBooks.ir
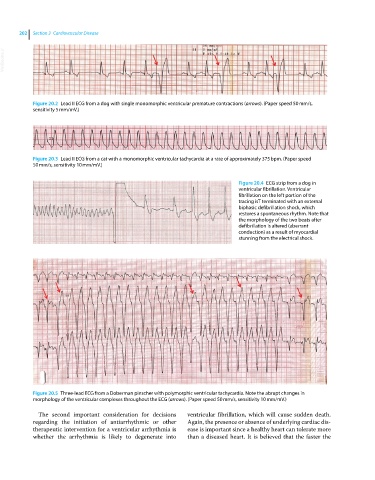
Figure 20.2 Lead II ECG from a dog with single monomorphic ventricular premature contractions (arrows). (Paper speed 50 mm/s,
sensitivity 5 mm/mV.)
Figure 20.3 Lead II ECG from a cat with a monomorphic ventricular tachycardia at a rate of approximately 375 bpm. (Paper speed
50 mm/s, sensitivity 10 mm/mV.)
Figure 20.4 ECG strip from a dog in
ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular
fibrillation on the left portion of the
tracing isT terminated with an external
biphasic defibrillation shock, which
restores a spontaneous rhythm. Note that
the morphology of the two beats after
defibrillation is altered (aberrant
conduction) as a result of myocardial
stunning from the electrical shock.
Figure 20.5 Three‐lead ECG from a Doberman pinscher with polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Note the abrupt changes in
morphology of the ventricular complexes throughout the ECG (arrows). (Paper speed 50 mm/s, sensitivity 10 mm/mV.)
The second important consideration for decisions ventricular fibrillation, which will cause sudden death.
regarding the initiation of antiarrhythmic or other Again, the presence or absence of underlying cardiac dis-
therapeutic intervention for a ventricular arrhythmia is ease is important since a healthy heart can tolerate more
whether the arrhythmia is likely to degenerate into than a diseased heart. It is believed that the faster the