Page 288 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 288
256 Section 3 Cardiovascular Disease
had at least one VPC on a 5‐min ECG and during echo severe cases). The distribution of pulmonary edema is
VetBooks.ir exam, respectively, emphasizing that many affected dogs often greatest in the caudodorsal lung fields, but can be
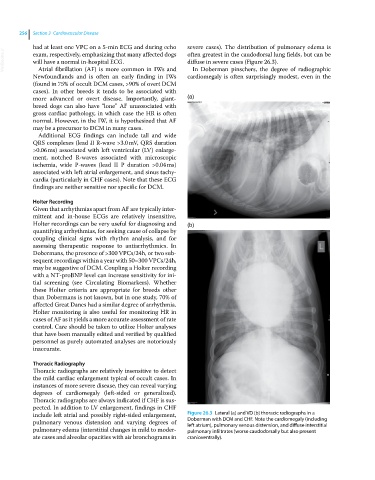
diffuse in severe cases (Figure 26.3).
will have a normal in‐hospital ECG.
In Doberman pinschers, the degree of radiographic
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is more common in IWs and
Newfoundlands and is often an early finding in IWs cardiomegaly is often surprisingly modest, even in the
(found in 75% of occult DCM cases, >90% of overt DCM
cases). In other breeds it tends to be associated with
more advanced or overt disease. Importantly, giant‐ (a)
breed dogs can also have “lone” AF unassociated with
gross cardiac pathology, in which case the HR is often
normal. However, in the IW, it is hypothesized that AF
may be a precursor to DCM in many cases.
Additional ECG findings can include tall and wide
QRS complexes (lead II R‐wave >3.0 mV, QRS duration
>0.06 ms) associated with left ventricular (LV) enlarge-
ment, notched R‐waves associated with microscopic
ischemia, wide P‐waves (lead II P duration >0.04 ms)
associated with left atrial enlargement, and sinus tachy-
cardia (particularly in CHF cases). Note that these ECG
findings are neither sensitive nor specific for DCM.
Holter Recording
Given that arrhythmias apart from AF are typically inter-
mittent and in‐house ECGs are relatively insensitive,
Holter recordings can be very useful for diagnosing and (b)
quantifying arrhythmias, for seeking cause of collapse by
coupling clinical signs with rhythm analysis, and for
assessing therapeutic response to antiarrhythmics. In
Dobermans, the presence of >300 VPCs/24h, or two sub-
sequent recordings within a year with 50–300 VPCs/24h,
may be suggestive of DCM. Coupling a Holter recording
with a NT‐proBNP level can increase sensitivity for ini-
tial screening (see Circulating Biomarkers). Whether
these Holter criteria are appropriate for breeds other
than Dobermans is not known, but in one study, 70% of
affected Great Danes had a similar degree of arrhythmia.
Holter monitoring is also useful for monitoring HR in
cases of AF as it yields a more accurate assessment of rate
control. Care should be taken to utilize Holter analyses
that have been manually edited and verified by qualified
personnel as purely automated analyses are notoriously
inaccurate.
Thoracic Radiography
Thoracic radiographs are relatively insensitive to detect
the mild cardiac enlargement typical of occult cases. In
instances of more severe disease, they can reveal varying
degrees of cardiomegaly (left‐sided or generalized).
Thoracic radiographs are always indicated if CHF is sus-
pected. In addition to LV enlargement, findings in CHF
include left atrial and possibly right‐sided enlargement, Figure 26.3 Lateral (a) and VD (b) thoracic radiographs in a
pulmonary venous distension and varying degrees of Doberman with DCM and CHF. Note the cardiomegaly (including
left atrium), pulmonary venous distension, and diffuse interstitial
pulmonary edema (interstitial changes in mild to moder- pulmonary infiltrates (worse caudodorsally but also present
ate cases and alveolar opacities with air bronchograms in cranioventrally).