Page 570 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 570
538 Section 6 Gastrointestinal Disease
(a) (c) (d)
VetBooks.ir
(b) (e)
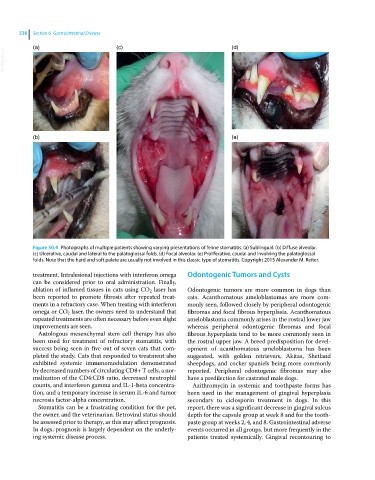
Figure 50.4 Photographs of multiple patients showing varying presentations of feline stomatitis. (a) Sublingual. (b) Diffuse alveolar.
(c) Ulcerative, caudal and lateral to the palatoglossal folds. (d) Focal alveolar. (e) Proliferative, caudal and involving the palatoglossal
folds. Note that the hard and soft palate are usually not involved in this classic type of stomatitis. Copyright 2015 Alexander M. Reiter.
treatment. Intralesional injections with interferon omega Odontogenic Tumors and Cysts
can be considered prior to oral administration. Finally,
ablation of inflamed tissues in cats using CO 2 laser has Odontogenic tumors are more common in dogs than
been reported to promote fibrosis after repeated treat cats. Acanthomatous ameloblastomas are more com
ments in a refractory case. When treating with interferon monly seen, followed closely by peripheral odontogenic
omega or CO 2 laser, the owners need to understand that fibromas and focal fibrous hyperplasia. Acanthomatous
repeated treatments are often necessary before even slight ameloblastoma commonly arises in the rostral lower jaw
improvements are seen. whereas peripheral odontogenic fibromas and focal
Autologous mesenchymal stem cell therapy has also fibrous hyperplasia tend to be more commonly seen in
been used for treatment of refractory stomatitis, with the rostral upper jaw. A breed predisposition for devel
success being seen in five out of seven cats that com opment of acanthomatous ameloblastoma has been
pleted the study. Cats that responded to treatment also suggested, with golden retrievers, Akitas, Shetland
exhibited systemic immunomodulation demonstrated sheepdogs, and cocker spaniels being more commonly
by decreased numbers of circulating CD8+ T cells, a nor reported. Peripheral odontogenic fibromas may also
malization of the CD4:CD8 ratio, decreased neutrophil have a predilection for castrated male dogs.
counts, and interferon gamma and IL‐1‐beta concentra Azithromycin in systemic and toothpaste forms has
tion, and a temporary increase in serum IL‐6 and tumor been used in the management of gingival hyperplasia
necrosis factor‐alpha concentration. secondary to ciclosporin treatment in dogs. In this
Stomatitis can be a frustrating condition for the pet, report, there was a significant decrease in gingival sulcus
the owner, and the veterinarian. Retroviral status should depth for the capsule group at week 8 and for the tooth
be assessed prior to therapy, as this may affect prognosis. paste group at weeks 2, 4, and 8. Gastrointestinal adverse
In dogs, prognosis is largely dependent on the underly events occurred in all groups, but more frequently in the
ing systemic disease process. patients treated systemically. Gingival recontouring to