Page 174 - Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition
P. 174
176 Small Animal Clinical Nutrition
Table 8-9. Common pet food additives.*
VetBooks.ir Antioxidant preservatives red [FD&C red No. 40]) Water (moisture)
Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA)
Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) Caramel color Whey
Iron oxide
Emulsifying agents, stabilizers and
Ethoxyquin Natural color(s) thickeners
Propyl gallate Nonazo dyes (brilliant blue [FD&C blue No. Diglycerides (of edible fats and oils)
Rosemaric acid/rosmarequinone 1], indigotin [FD&C blue No. 2]) Glycerin
Tocopherols Sodium erythrobate Glyceryl monostearate
Antimicrobial preservatives Sodium metabisulfite Gums (hydrocolloids)
Calcium propionate Sodium nitrite Seaweed extracts (carrageenan, algi-
Citric acid Titanium dioxide nates)
Fumaric acid Flavors/flavor enhancers Seed gums (guar gum)
Hydrochloric acid Artificial flavors Microbial gums (xanthan gum)
Phosphoric acid Citrus bioflavonoids Chemically modified plant materials
Potassium sorbate Dehydrated cheese/dried cheese powder Modified starch
Propionic acid Digests Monoglycerides (of edible fats and oils)
Pyroligneous acid Liver meal Miscellaneous
Sodium nitrite Monosodium glutamate Charcoal
Sodium propionate Natural flavors Mineral oil (reduces dust)
Sorbic acid Natural smoke flavor Polyphosphates (dental calculus preven-
Humectants Palatability enhancers tion)
Cane molasses Acidified yeast Sodium tripolyphosphate
Corn syrups Digests (dough conditioner)
Propylene glycol Garlic powder/oil Disodium phosphate
Sorbitol Hydrochloric acid Tetrasodium pyrophosphate
Sucrose/dextrose L-lysine Yucca schidigera extract (flavor,
Coloring agents/preservatives Meat extracts (beef, chicken, turkey) odor control)
Aluminum potassium sulfate Onion powder/oil *Adapted from Roudebush P. Pet food
Artificial color(s) Phosphoric acid additives. Journal of the American
Azo dyes (tartrazine [FD&C yellow No. 5], Spices Veterinary Medical Association 1993; 203:
sunset yellow [FD&C yellow No. 6], allura Sucrose, dextrose, cane molasses 1667-1670.
most important and beneficial use of pet food additives. Most
ingredients with unfamiliar, chemical-sounding names are, in
fact, nutrients. In general, additives other than vitamins and
minerals are found least often or in smallest amounts in moist
foods, and most commonly or in largest amounts in dry foods,
semi-moist foods, treats and snacks.
The term “additive” is inclusive for anything imparting
increased nutritional, gustatory or cosmetic appeal. Additives
commonly used in prepared human and pet foods include col-
ors, flavors, flavor enhancers, emulsifying agents, gelling sub-
stances, stabilizers, thickeners and processing aids. The terms
preservative and additive are often used synonymously, but they
are distinctly different. Preservatives are substances added to
foods to protect or retard decay, discoloration or spoilage under
normal use or storage conditions. Thus, all preservatives are
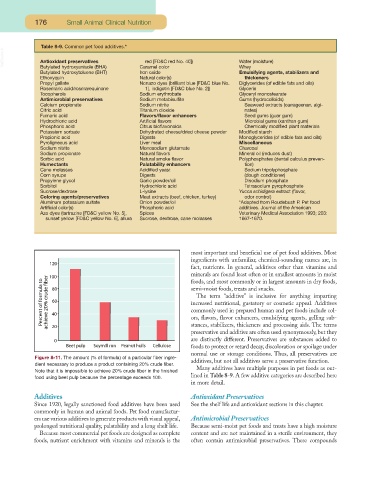
Figure 8-11. The amount (% of formula) of a particular fiber ingre-
additives, but not all additives serve a preservative function.
dient necessary to produce a product containing 20% crude fiber.
Many additives have multiple purposes in pet foods as out-
Note that it is impossible to achieve 20% crude fiber in the finished
lined in Table 8-9. A few additive categories are described here
food using beet pulp because the percentage exceeds 100.
in more detail.
Additives Antioxidant Preservatives
Since 1920, legally sanctioned food additives have been used See the shelf life and antioxidant sections in this chapter.
commonly in human and animal foods. Pet food manufactur-
ers use various additives to generate products with visual appeal, Antimicrobial Preservatives
prolonged nutritional quality, palatability and a long shelf life. Because semi-moist pet foods and treats have a high moisture
Because most commercial pet foods are designed as complete content and are not maintained in a sterile environment, they
foods, nutrient enrichment with vitamins and minerals is the often contain antimicrobial preservatives. These compounds