Page 179 - Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition
P. 179
Commercial Pet Foods 181
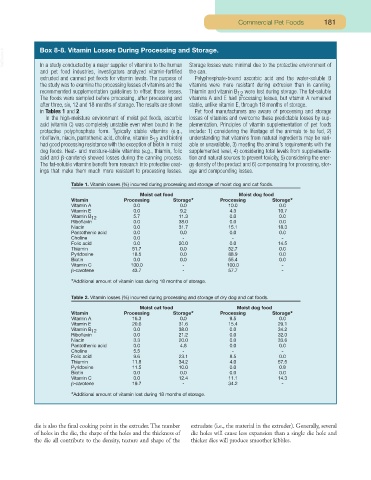
VetBooks.ir Box 8-8. Vitamin Losses During Processing and Storage.
In a study conducted by a major supplier of vitamins to the human
and pet food industries, investigators analyzed vitamin-fortified Storage losses were minimal due to the protective environment of
the can.
extruded and canned pet foods for vitamin levels. The purpose of Polyphosphate-bound ascorbic acid and the water-soluble B
the study was to examine the processing losses of vitamins and the vitamins were more resistant during extrusion than in canning.
recommended supplementation guidelines to offset those losses. Thiamin and vitamin B 12 were lost during storage. The fat-soluble
The foods were sampled before processing, after processing and vitamins A and E had processing losses, but vitamin A remained
after three, six, 12 and 18 months of storage.The results are shown stable, unlike vitamin E, through 18 months of storage.
in Tables 1 and 2. Pet food manufacturers are aware of processing and storage
In the high-moisture environment of moist pet foods, ascorbic losses of vitamins and overcome these predictable losses by sup-
acid (vitamin C) was completely unstable even when bound in the plementation. Principles of vitamin supplementation of pet foods
protective polyphosphate form. Typically stable vitamins (e.g., include: 1) considering the lifestage of the animals to be fed, 2)
riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, choline, vitamin B 12 and biotin) understanding that vitamins from natural ingredients may be vari-
had good processing resistance with the exception of biotin in moist able or unavailable, 3) meeting the animal’s requirements with the
dog foods. Heat- and moisture-labile vitamins (e.g., thiamin, folic supplemented level, 4) considering total levels from supplementa-
acid and β-carotene) showed losses during the canning process. tion and natural sources to prevent toxicity, 5) considering the ener-
The fat-soluble vitamins benefit from research into protective coat- gy density of the product and 6) compensating for processing, stor-
ings that make them much more resistant to processing losses. age and compounding losses.
Table 1. Vitamin losses (%) incurred during processing and storage of moist dog and cat foods.
Moist cat food Moist dog food
Vitamin Processing Storage* Processing Storage*
Vitamin A 0.0 0.0 10.0 0.0
Vitamin E 0.0 9.2 4.3 10.7
Vitamin B 12 5.7 11.3 0.0 0.0
Riboflavin 0.0 38.0 0.0 0.0
Niacin 0.0 31.7 15.1 18.3
Pantothenic acid 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Choline 0.0 - - -
Folic acid 0.0 20.0 0.0 14.5
Thiamin 51.7 0.0 52.7 0.0
Pyridoxine 18.5 0.0 88.9 0.0
Biotin 0.0 0.0 55.4 0.0
Vitamin C 100.0 - 100.0 -
β-carotene 43.7 - 57.7 -
*Additional amount of vitamin loss during 18 months of storage.
Table 2. Vitamin losses (%) incurred during processing and storage of dry dog and cat foods.
Moist cat food Moist dog food
Vitamin Processing Storage* Processing Storage*
Vitamin A 16.3 0.0 9.5 0.0
Vitamin E 20.6 31.6 15.4 29.1
Vitamin B 12 0.0 38.0 0.0 34.2
Riboflavin 0.0 21.2 0.0 32.0
Niacin 3.3 20.0 0.0 33.6
Pantothenic acid 0.0 4.8 0.0 0.0
Choline 5.5 - - -
Folic acid 9.6 23.1 8.5 0.0
Thiamin 11.8 34.2 4.0 57.5
Pyridoxine 11.5 10.0 0.0 0.8
Biotin 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Vitamin C 0.0 12.4 11.1 14.3
β-carotene 19.7 - 34.2 -
*Additional amount of vitamin lost during 18 months of storage.
die is also the final cooking point in the extruder. The number extrudate (i.e., the material in the extruder). Generally, several
of holes in the die, the shape of the holes and the thickness of die holes will cause less expansion than a single die hole and
the die all contribute to the density, texture and shape of the thicker dies will produce smoother kibbles.