Page 97 - Clinical Pearls in Cardiology
P. 97
Auscultation of the Precordium 85
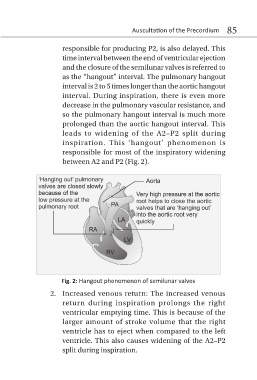
responsible for producing P2, is also delayed. This
time interval between the end of ventricular ejection
and the closure of the semilunar valves is referred to
as the “hangout” interval. The pulmonary hangout
interval is 2 to 5 times longer than the aortic hangout
interval. During inspiration, there is even more
decrease in the pulmonary vascular resistance, and
so the pulmonary hangout interval is much more
prolonged than the aortic hangout interval. This
leads to widening of the A2–P2 split during
inspiration. This ‘hangout’ phenomenon is
responsible for most of the inspiratory widening
between A2 and P2 (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2: Hangout phenomenon of semilunar valves
2. Increased venous return: The increased venous
return during inspiration prolongs the right
ventricular emptying time. This is because of the
larger amount of stroke volume that the right
ventricle has to eject when compared to the left
ventricle. This also causes widening of the A2–P2
split during inspiration.