Page 6 - Life Insurance Today March 2016
P. 6
To understand the concept of understand and access those services. Apart from the regular form of finan-
PMJDY. cial intermediation, it may include a basic no frills banking account for making
and receiving payments, a savings product suited to the pattern of cash flows
To know the progress of PMJDY in of a poor household, money transfer facilities, small loans and overdrafts for
general and particularly with ref- productive, personal and other purposes.
erence to state of Karnataka.
Inclusive growth in India: Methodology:
In India, the government and the RBI The study is purely based on secondary data. The data are collected from jour-
have been promoting the necessity of nals, newspapers, reports and website.
inclusive banking as a collective body,
has been taking several initiatives in Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana:
this regard. At the all India level, less
than 5 per cent of poor rural house- PMJDY is an initiative of financial inclusion which was announced by the hon-
holds have access to microfinance as orable Prime Minister on 15th August 2014 and launched by him on 28th Au-
compared to 60 per cent in gust 2014 across the country. It is for the first time in history of banking sec-
Bangaladesh. The Southern states tor, the inclusive practice has adopted. Through this, inclusion process received
account for almost 75 per cent of a new boost by Government of India.
funds flowing under Micro Finance
programmes. The situation survey of The objective of PMJDY is ensuring access to various financial services like avail-
Farmers was conducted in 2003 which ability of basic savings bank account, access to need based credit, remittance
indicated that the rural households facility, insurance and pension to the excluded schemes i.e. weaker sections
were at 147.90 million and out of it and low income groups. This deep penetration at affordable cost is possible
89.35 million were farmer house- only with effective use of technology.
holds. Data indicated that 51.4 per
cent of the farmer households were PMJDY is a national mission on financial inclusion encompassing an integrated
financially excluded. approach to bring comprehensive financial inclusion of all the households in
the country. The plan envisages universal access to banking facilities with at
According to the RAFS 2003, 41 per least one basic banking account for every household, financial literacy, access
cent of rural households have a de- to credit, insurance and pension facility. In addition, the beneficiaries would
posit account from formal banks serve get RuPay Debit card having inbuilt accident insurance covers of Rs 1lakh. The
the primary needs of the rich rural bor- plan also envisages universal access to banking facilities.
rowers; 66 per cent of large farmers
have a deposit account and 44 per Progress of PMJDY:
cent have access to credit. Meanwhile,
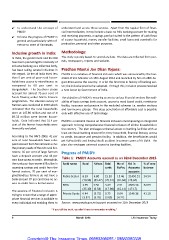
the rural poor face severe difficulties in Table 1: PMJDY Accounts opened as on 02nd December 2015
accessing savings and credit from the
formal sectors; 70 per cent of mar- Bank name Rural Urban Total No of Bal in % of zero
ginal/landless farmers do not have a cards RuPay Accounts balance
bank account 87 per cent have no ac-
cess to credit from a formal sector. Public Sector 8.39 6.80 15.20 accounts 34.54
RRBs (70.98) (89.47) (78.31)
The essence of financial inclusion is Private Banks 13.46 21450.31 32.09
trying to ensure that a range of appro- 2.99 0.50 3.49 (81.04) (78.62)
priate financial services is available to (25.30) (6.58) (17.98) 41.10
every individual and enabling them to 2.51 4683.38
0.44 (3.72) 0.73 (15.11) (17.17)
(3.82) (3.76) (3.85)
0.64 1149.36
(4.21)
Source: www.pmjdy.gov.in/account accessed on 11th December 2015
"If you tell the truth, you don't have to remember anything."
6 March 2016 Life Insurance Today