Page 25 - Essential Haematology
P. 25
Chapter 1 Haemopoiesis / 11
which phosophorylate downstream protein targets
M phase
and cyclins which bind to Cdks and regulate their
activity. An example of the importance of these
systems is demonstrated by mantle cell lymphoma
which results from the constitutive activation of
M
G 0 cyclin D1 as a result of a chromosomal translocation
Cdk2 (see p. 267 ).
G 1
G 2
Cdk2
Cyclin Cyclin
B
S E
Apoptosis
Cyclin
Cdk2
A
Apoptosis (programmed cell death) is a regulated
Interphase process of physiological cell death in which indi-
(a)
vidual cells are triggered to activate intracellular
proteins that lead to the death of the cell.
Morphologically it is characterized by cell shrink-
age, condensation of the nuclear chromatin, frag-
DNA content 4c mentation of the nucleus and cleavage of DNA at
internucleosomal sites. It is an important process for
lymphocyte development.
2c maintaining tissue homeostasis in haemopoiesis and
Apoptosis results from the action of intracellular
G 1 S G 2 M
cysteine proteases called caspases which are acti-
vated following cleavage and lead to endonuclease
Phase of cell cycle
(b) digestion of DNA and disintegration of the cell
skeleton (Fig. 1.11 ). There are two major pathways
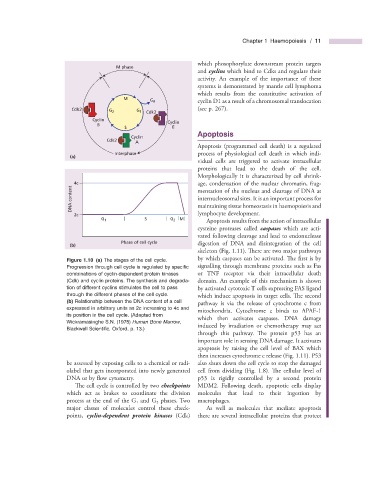
Figure 1.10 (a) The stages of the cell cycle. by which caspases can be activated. Th e first is by
Progression through cell cycle is regulated by specifi c signalling through membrane proteins such as Fas
combinations of cyclin - dependent protein kinases or TNF receptor via their intracellular death
(Cdk) and cyclin proteins. The synthesis and degrada- domain. An example of this mechanism is shown
tion of different cyclins stimulates the cell to pass by activated cytotoxic T cells expressing FAS ligand
through the different phases of the cell cycle. which induce apoptosis in target cells. Th e second
(b) Relationship between the DNA content of a cell
pathway is via the release of cytochrome c from
expressed in arbitrary units as 2c increasing to 4c and
mitochondria. Cytochrome c binds to APAF - 1
its position in the cell cycle. (Adapted from
which then activates caspases. DNA damage
Wickramasinghe S.N. (1975) Human Bone Marrow ,
induced by irradiation or chemotherapy may act
Blackwell Scientifi c, Oxford, p. 13.)
through this pathway. The protein p53 has an
important role in sensing DNA damage. It activates
apoptosis by raising the cell level of BAX which
then increases cytochrome c release (Fig. 1.11 ). P53
be assessed by exposing cells to a chemical or radi- also shuts down the cell cycle to stop the damaged
olabel that gets incorporated into newly generated cell from dividing (Fig. 1.8 ). Th e cellular level of
DNA or by fl ow cytometry. p53 is rigidly controlled by a second protein
The cell cycle is controlled by two checkpoints MDM2. Following death, apoptotic cells display
which act as brakes to coordinate the division molecules that lead to their ingestion by
process at the end of the G 1 and G 2 phases. Two macrophages.
major classes of molecules control these check- As well as molecules that mediate apoptosis
points, cyclin - dependent protein kinases (Cdk) there are several intracellular proteins that protect