Page 309 - Essential Haematology
P. 309
Chapter 22 Aplastic anaemia and bone marrow failure / 295
antibodies (e.g. Campath (anti - CD52) or rituximab neutropenia with a propensity to transform to mye-
(anti - CD20)) are being increasingly used in treat- lodysplasia or acute myeloid leukaemia. Exocrine
ment of refractory acquired red cell aplasia and pancreatic dysfunction is an invariable feature while
other autoimmune cytopenias. skeletal abnormalities, hepatic impairment and
If regular blood transfusions are needed, iron short stature are frequent. The gene SBDS, involved
chelation therapy will also be necessary. SCT has in ribosome synthesis, shows mutations (Fig. 22.3 ).
been carried out in some severe cases.
Transient Congenital d yserythropoietic
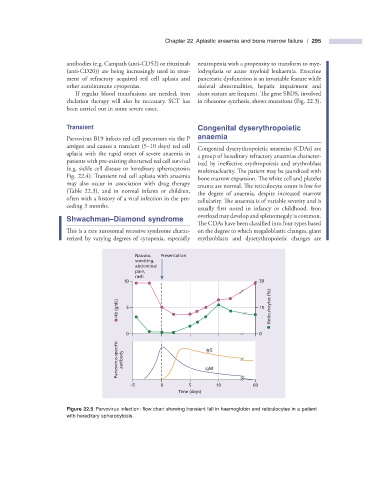
Parvovirus B19 infects red cell precursors via the P a naemia
antigen and causes a transient (5 – 10 days) red cell
Congenital dyserythropoietic anaemias (CDAs) are
aplasia with the rapid onset of severe anaemia in
a group of hereditary refractory anaemias character-
patients with pre - existing shortened red cell survival
ized by ineffective erythropoiesis and erythroblast
(e.g. sickle cell disease or hereditary spherocytosis;
multinuclearity. The patient may be jaundiced with
Fig. 22.4 ). Transient red cell aplasia with anaemia
bone marrow expansion. The white cell and platelet
may also occur in association with drug therapy
counts are normal. The reticulocyte count is low for
(Table 22.3 ), and in normal infants or children,
the degree of anaemia, despite increased marrow
often with a history of a viral infection in the pre-
cellularity. The anaemia is of variable severity and is
ceding 3 months.
usually first noted in infancy or childhood. Iron
overload may develop and splenomegaly is common.
Shwachman – Diamond s yndrome
The CDAs have been classified into four types based
This is a rare autosomal recessive syndrome charac- on the degree to which megaloblastic changes, giant
terized by varying degrees of cytopenia, especially erythroblasts and dyserythropoietic changes are
Nausea, Presentation
vomiting,
abdominal
pain,
rash
10 30
Hb (g/dL) 5 15 Reticulocytes (%)
0 0
Parvovirus-specific antibody IgM
IgG
–5 0 5 10 60
Time (days)
Figure 22.5 Parvovirus infection: fl ow chart showing transient fall in haemoglobin and reticulocytes in a patient
with hereditary spherocytosis.