Page 305 - Essential Haematology
P. 305
Chapter 22 Aplastic anaemia and bone marrow failure / 291
Cells from patients with Fanconi s anaemia (FA) Dyskeratosis congenita (DC) is a rare sex -
’
show an abnormally high frequency of spontaneous linked disorder with nail and skin atrophy, aplastic
chromosomal breakage and the diagnostic test is anaemia and a high risk of cancer. It is associated
elevated breakage after incubation of peripheral with mutations in the DKC1 (dyskerin) or TERC
blood lymphocytes with the DNA cross - linking (telomerase reverse transcriptase RNA template)
agent diepoxybutane (DEB test). genes which are both involved in the maintenance
The usual age of presentation of FA is 5 – 10 of telomere length.
years. Approximately 10% of patients develop acute Other inherited bone marrow failure syndromes
myeloid leukaemia. Treatment is usually with include Diamond – Blackfan anaemia (DBA), (see p.
androgens and/or SCT. The blood count usually 294) , Shwachman – Diamond syndrome (SDS),
improves with androgens but side - eff ects, especially (see p. 295), severe congenital neutropenia (see
in children, are distressing (virilization and liver p. 119), amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (see
abnormalities); remission rarely lasts more than 2 p. 333) and thrombocytopenia with absent radii
years. SCT may cure the patient. Because of the (see p. 333) . In DC, DBA and SDS there are
sensitivity of the patient s cells to DNA damage, defects in ribosomal biosynthesis and function
’
conditioning regimens are mild. (Fig. 22.3 ).
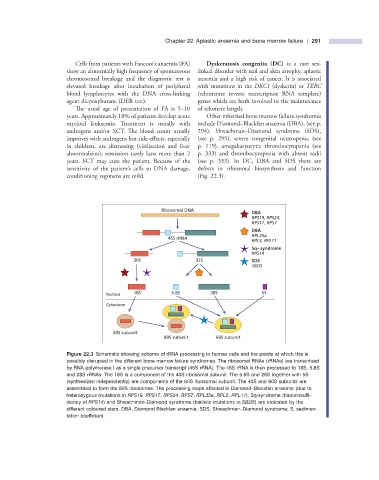
Ribosomal DNA
DBA
RPS19, RPS24,
RPS17, RPS7
DBA
RPL35a,
45S rRNA
RPL5, RPL11
5q– syndrome
RPS14
30S 32S SDS
SBDS
Nucleus 18S 5.8S 28S 5S
Cytoplasm
40S subunit
80S subunit 60S subunit
Figure 22.3 Schematic showing scheme of rRNA processing in human cells and the points at which this is
possibly disrupted in the different bone marrow failure syndromes. The ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) are transcribed
by RNA polymerase I as a single precursor transcript (45S rRNA). The 45S rRNA is then processed to 18S, 5.8S
and 28S rRNAs. The 18S is a component of the 40S ribosomal subunit. The 5.8S and 28S together with 5S
(synthesized independently) are components of the 60S ribosomal subunit. The 40S and 60S subunits are
assembled to form the 80S ribosomes. The processing steps affected in Diamond – Blackfan anaemia (due to
heterozygous mutations in RPS19, RPS17 , RPS24 , RPS7 , RPL35a , RPL5 , RPL11 ), 5q - syndrome (haploinsuffi -
ciency of RPS14 ) and Shwachman – Diamond syndrome (biallelic mutations in SBDS ) are indicated by the
different coloured stars. DBA, Diamond Blackfan anaemia; SDS, Shwachman – Diamond syndrome; S, sedimen-
tation coeffi cient.