Page 318 - Essential Haematology
P. 318
304 / Chapter 23 Stem cell transplantation
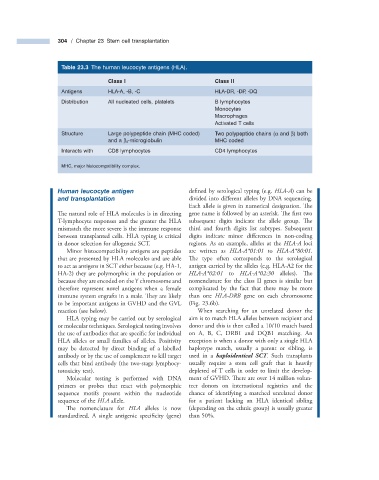
Table 23.3 The human leucocyte antigens (HLA).
Class I Class II
Antigens HLA - A, - B, - C HLA - DR, - DP, - DQ
Distribution All nucleated cells, platelets B lymphocytes
Monocytes
Macrophages
Activated T cells
Structure Large polypeptide chain (MHC coded) Two polypeptide chains ( α and β ) both
- microglobulin MHC coded
and a β 2
Interacts with CD8 lymphocytes CD4 lymphocytes
MHC, major histocompatibility complex.
Human l eucocyte a ntigen defined by serological typing (e.g. HLA - A ) can be
and t ransplantation divided into different alleles by DNA sequencing.
Each allele is given in numerical designation. Th e
The natural role of HLA molecules is in directing gene name is followed by an asterisk. Th e fi rst two
T - lymphocyte responses and the greater the HLA subsequent digits indicate the allele group. Th e
mismatch the more severe is the immune response third and fourth digits list subtypes. Subsequent
between transplanted cells. HLA typing is critical digits indicate minor diff erences in non - coding
in donor selection for allogeneic SCT. regions. As an example, alleles at the HLA - A loci
Minor histocompatibility antigens are peptides are written as HLA - A * 01:01 to HLA - A * 80:01 .
that are presented by HLA molecules and are able Th e type often corresponds to the serological
to act as antigens in SCT either because (e.g. HA - 1, antigen carried by the alleles (e.g. HLA - A2 for the
HA - 2) they are polymorphic in the population or HLA - A * 02:01 to HLA - A * 02:30 alleles). Th e
because they are encoded on the Y chromosome and nomenclature for the class II genes is similar but
therefore represent novel antigens when a female complicated by the fact that there may be more
immune system engrafts in a male. They are likely than one HLA - DRB gene on each chromosome
to be important antigens in GVHD and the GVL (Fig. 23.6 b).
reaction (see below). When searching for an unrelated donor the
HLA typing may be carried out by serological aim is to match HLA alleles between recipient and
or molecular techniques. Serological testing involves donor and this is then called a 10/10 match based
the use of antibodies that are specific for individual on A, B, C, DRB1 and DQB1 matching. An
HLA alleles or small families of alleles. Positivity exception is when a donor with only a single HLA
may be detected by direct binding of a labelled haplotype match, usually a parent or sibling, is
antibody or by the use of complement to kill target used in a haploidentical SCT . Such transplants
cells that bind antibody (the two - stage lymphocy- usually require a stem cell graft that is heavily
totoxicity test). depleted of T cells in order to limit the develop-
Molecular testing is performed with DNA ment of GVHD. Th ere are over 14 million volun-
primers or probes that react with polymorphic teer donors on international registries and the
sequence motifs present within the nucleotide chance of identifying a matched unrelated donor
sequence of the HLA allele. for a patient lacking an HLA identical sibling
The nomenclature for HLA alleles is now (depending on the ethnic group) is usually greater
standardized. A single antigenic specifi city (gene) than 50%.