Page 320 - Essential Haematology
P. 320
306 / Chapter 23 Stem cell transplantation
Chimerism a nalysis these tissues are involved but also the joints and
other serosal surfaces, the oral mucosa and lacrimal
’
Following allogeneic SCT, the recipient s blood
glands. Features of scleroderma, Sj ö gren s syndrome
’
shows the presence of both donor and recipient
and lichen planus may develop. The immune system
cells (chimerism). This can be by fl uorescence
is impaired (including hyposplenism) with risk of
in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis of the
proportion of Y chromosome containing cells if
there is a sex mismatch or by DNA analysis
techniques.
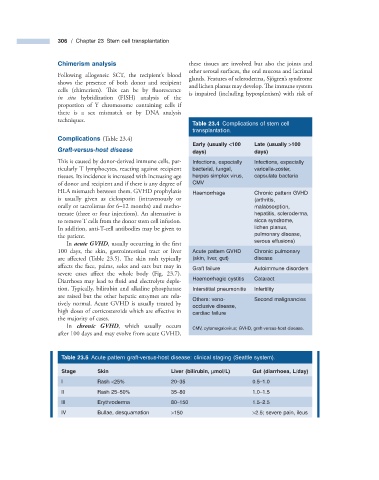
Table 23.4 Complications of stem cell
transplantation.
Complications (Table 23.4 )
Early (usually < 100 Late (usually > 100
Graft - v ersus - h ost d isease days) days)
This is caused by donor - derived immune cells, par- Infections, especially Infections, especially
ticularly T lymphocytes, reacting against recipient bacterial, fungal, varicella - zoster,
tissues. Its incidence is increased with increasing age herpes simplex virus, capsulate bacteria
of donor and recipient and if there is any degree of CMV
HLA mismatch between them. GVHD prophylaxis Haemorrhage Chronic pattern GVHD
is usually given as ciclosporin (intravenously or (arthritis,
orally or tacrolimus for 6 – 12 months) and metho- malabsorption,
trexate (three or four injections). An alternative is hepatitis, scleroderma,
to remove T cells from the donor stem cell infusion. sicca syndrome,
In addition, anti - T - cell antibodies may be given to lichen planus,
the patient. pulmonary disease,
In acute GVHD , usually occurring in the fi rst serous effusions)
100 days, the skin, gastrointestinal tract or liver Acute pattern GVHD Chronic pulmonary
are affected (Table 23.5 ). The skin rash typically (skin, liver, gut) disease
affects the face, palms, soles and ears but may in
Graft failure Autoimmune disorders
severe cases affect the whole body (Fig. 23.7 ).
Diarrhoea may lead to fluid and electrolyte deple- Haemorrhagic cystitis Cataract
tion. Typically, bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase Interstitial pneumonitis Infertility
are raised but the other hepatic enzymes are rela-
Others: veno - Second malignancies
tively normal. Acute GVHD is usually treated by
occlusive disease,
high doses of corticosteroids which are eff ective in cardiac failure
the majority of cases.
In chronic GVHD , which usually occurs
CMV, cytomegalovirus; GVHD, graft - versus - host disease.
after 100 days and may evolve from acute GVHD,
Table 23.5 Acute pattern graft - versus - host disease: clinical staging (Seattle system).
Stage Skin Liver (bilirubin, μ mol/L) Gut (diarrhoea, L/day)
I Rash < 25% 20 – 35 0.5 – 1.0
II Rash 25 – 50% 35 – 80 1.0 – 1.5
III Erythroderma 80 – 150 1.5 – 2.5
IV Bullae, desquamation > 150 > 2.5; severe pain, ileus