Page 323 - Essential Haematology
P. 323
Chapter 23 Stem cell transplantation / 309
(VZV) occurring at different peak intervals (Fig. and foscarnet may be used for established CMV
23.8 ). infection.
CMV presents a particular threat and is associ- VZV infection is also frequent post - SCT but
ated with a potentially fatal interstitial pneumonitis occurs later with a median onset at 4 – 5 months.
as well as with hepatitis and falling blood counts. Rarely, disseminated VZV infection occurs.
The infection may be caused by reactivation of Intravenous aciclovir is indicated. Epstein – Barr
CMV in the recipient or a new infection transmit- virus (EBV) infections and EBV - associated lympho-
ted by the donor. In CMV - seronegative patients proliferative disease are less frequent after SCT than
with CMV - seronegative donors, CMV - negative after solid organ transplants.
blood products or leucodepleted blood must Pneumocystis carinii is another cause of pneumo-
be given. Aciclovir may be useful in prophylaxis. nitis that may be prevented by prophylactic co -
Most centres screen patients regularly for evidence trimoxazole or pentamidine inhalations.
of CMV reactivation following allogeneic trans-
plantation using polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
or antibody - based tests. If these tests become Interstitial p neumonitis
positive, ganciclovir may suppress the virus This is one of the most frequent causes of death
before disease occurs. Ganciclovir, valganciclovir post - SCT (Fig. 23.10 ). CMV is a frequent agent
(b)
(a) (c)
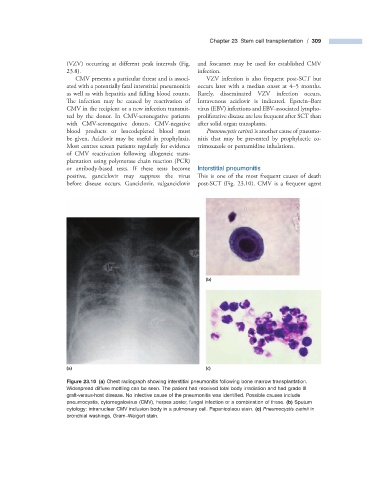
Figure 23.10 (a) Chest radiograph showing interstitial pneumonitis following bone marrow transplantation.
Widespread diffuse mottling can be seen. The patient had received total body irradiation and had grade III
graft - versus - host disease. No infective cause of the pneumonitis was identifi ed. Possible causes include
pneumocystis, cytomegalovirus (CMV), herpes zoster, fungal infection or a combination of these. (b) Sputum
cytology: intranuclear CMV inclusion body in a pulmonary cell. Papanicolaou stain. (c) Pneumocystis carinii in
bronchial washings, Gram – Weigert stain.