Page 399 - Essential Haematology
P. 399
Chapter 28 Haematological changes in systemic disease / 385
bleeding, interruptions with chemotherapy and In systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) there
thrombocytopenia, anorexia or vomiting. Liver may be anaemia of chronic disorders and 50% of
disease and drug interactions can cause further patients are leucopenic with reduced neutrophil and
complications so daily low molecular weight heparin lymphocyte counts often associated with circulating
injections may be preferable to oral anticoagulants. immune complexes. Renal impairment and drug -
induced gastrointestinal blood loss also contribute
Rheumatoid a rthritis (and o ther to the anaemia. Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia
c onnective t issue d isorders) (typically with immunoglobulin G (IgG) and the
C3 component of complement on the surface of the
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, the anaemia
red cells) occurs in 5% of patients and may be the
of chronic disorders is proportional to the severity
presenting feature of the syndrome. There may be
of the disease. It is complicated in some patients
autoimmune thrombocytopenia in 5% of patients.
by iron deficiency caused by gastrointestinal bleed-
The lupus anticoagulant is described on p. 369 . Th is
ing related to therapy with salicylates, other non -
circulating anticardiolipin interferes with blood
steroidal anti - inflammatory agents or corticosteroids.
coagulation by altering the binding of coagulation
Bleeding into inflamed joints may also be a factor.
factors to platelet phospholipid and predisposes to
Marrow hypoplasia may follow therapy with gold.
both arterial and venous thrombosis and recurrent
’
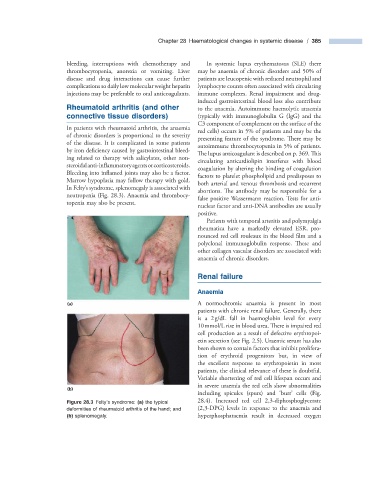
In Felty s syndrome, splenomegaly is associated with
abortions. The antibody may be responsible for a
neutropenia (Fig. 28.3 ). Anaemia and thrombocy-
false positive Wassermann reaction. Tests for anti-
topenia may also be present.
nuclear factor and anti - DNA antibodies are usually
positive.
Patients with temporal arteritis and polymyalgia
rheumatica have a markedly elevated ESR, pro-
nounced red cell rouleaux in the blood film and a
polyclonal immunoglobulin response. Th ese and
other collagen vascular disorders are associated with
anaemia of chronic disorders.
Renal f ailure
Anaemia
(a) A normochromic anaemia is present in most
patients with chronic renal failure. Generally, there
is a 2 g/dL fall in haemoglobin level for every
10 mmol/L rise in blood urea. There is impaired red
cell production as a result of defective erythropoi-
etin secretion (see Fig. 2.5 ). Uraemic serum has also
been shown to contain factors that inhibit prolifera-
tion of erythroid progenitors but, in view of
the excellent response to erythropoietin in most
patients, the clinical relevance of these is doubtful.
Variable shortening of red cell lifespan occurs and
in severe uraemia the red cells show abnormalities
(b)
including spicules (spurs) and ‘ burr ’ cells (Fig.
Figure 28.3 Felty ’ s syndrome: (a) the typical 28.4 ). Increased red cell 2,3 - diphosphoglycerate
deformities of rheumatoid arthritis of the hand; and (2,3 - DPG) levels in response to the anaemia and
(b) splenomegaly. hyperphosphataemia result in decreased oxygen