Page 398 - Essential Haematology
P. 398
384 / Chapter 28 Haematological changes in systemic disease
Table 28.2 Haematological abnormalities in malignant disease.
Haematological abnormality Tumour or treatment associated
Pancytopenia
Marrow hypoplasia Chemotherapy, radiotherapy
Myelodysplasia Chemotherapy, radiotherapy
Leucoerythroblastic Metastases in marrow
Megaloblastic Folate defi ciency
B 12 defi ciency (carcinoma of stomach)
Red cells
Anaemia of chronic disorders Most forms
Iron defi ciency anaemia Especially gastrointestinal, uterine
Pure red cell aplasia Thymoma
Immune haemolytic anaemia Lymphoma, ovary, other tumours
Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia Mucin - secreting carcinoma
Polycythaemia Kidney, liver, cerebellum, uterus
White cells
Neutrophil leucocytosis Most forms
Leukaemoid reaction Disseminated tumours, those with necrosis
Eosinophilia Hodgkin lymphoma, others
Monocytosis Various tumours
Platelets and coagulation
Thrombocytosis Gastrointestinal tumours with bleeding, others
Disseminated intravascular coagulation Mucin - secreting carcinoma, prostate
Activation of fi brinolysis Prostate
Acquired inhibitors of coagulation Most forms
Paraprotein interfering with platelet function Lymphomas, myeloma
Tumour cell procoagulants – tissue factor and Especially ovarian, pancreas, brain, colon
cancer procoagulant (activates factor X)
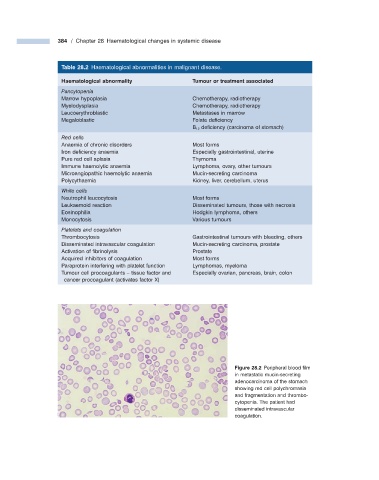
Figure 28.2 Peripheral blood fi lm
in metastatic mucin - secreting
adenocarcinoma of the stomach
showing red cell polychromasia
and fragmentation and thrombo-
cytopenia. The patient had
disseminated intravascular
coagulation.