Page 393 - Essential Haematology
P. 393
Chapter 27 Thrombosis and antithrombotic therapy / 379
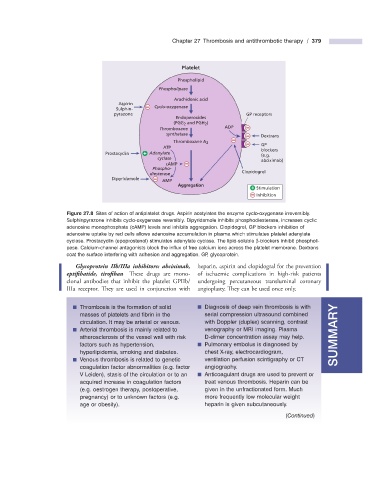
Platelet
Phospholipid
Phospholipase
Arachidonic acid
Aspirin
Cyclo-oxygenase
Sulphin-
pyrazone GP receptors
Endoperoxides
(PGG 2 and PGH 2 )
Thromboxane ADP
synthetase
Dextrans
Thromboxane A 2
GP
ATP
Prostacyclin Adenylate blockers
(e.g.
cyclase
abciximab)
cAMP
Phospho-
diesterase Clopidogrel
Dipyridamole AMP
Aggregation
Stimulation
Inhibition
Figure 27.8 Sites of action of antiplatelet drugs. Aspirin acetylates the enzyme cyclo - oxygenase irreversibly.
Sulphinpyrazone inhibits cyclo - oxygenase reversibly. Dipyridamole inhibits phosphodiesterase, increases cyclic
adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels and inhibits aggregation. Clopidogrel, GP blockers inhibition of
adenosine uptake by red cells allows adenosine accumulation in plasma which stimulates platelet adenylate
cyclase. Prostacyclin (epoprostenol) stimulates adenylate cyclase. The lipid - soluble β - blockers inhibit phospholi-
pase. Calcium - channel antagonists block the infl ux of free calcium ions across the platelet membrane. Dextrans
coat the surface interfering with adhesion and aggregation. GP, glycoprotein.
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors: abciximab, heparin, aspirin and clopidogral for the prevention
eptifi batide, tirofi ban These drugs are mono- of ischaemic complications in high - risk patients
clonal antibodies that inhibit the platelet GPIIb/ undergoing percutaneous transluminal coronary
IIIa receptor. They are used in conjunction with angioplasty. They can be used once only.
■ Thrombosis is the formation of solid ■ Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis is with
masses of platelets and fi brin in the serial compression ultrasound combined
circulation. It may be arterial or venous. with Doppler (duplex) scanning, contrast
■ Arterial thrombosis is mainly related to venography or MRI imaging. Plasma SUMMARY
atherosclerosis of the vessel wall with risk D - dimer concentration assay may help.
factors such as hypertension, ■ Pulmonary embolus is diagnosed by
hyperlipidemia, smoking and diabetes. chest X - ray, electrocardiogram,
■ Venous thrombosis is related to genetic ventilation perfusion scintigraphy or CT
coagulation factor abnormalities (e.g. factor angiography.
V Leiden), stasis of the circulation or to an ■ Anticoagulant drugs are used to prevent or
acquired increase in coagulation factors treat venous thrombosis. Heparin can be
(e.g. oestrogen therapy, postoperative, given in the unfractionated form. Much
pregnancy) or to unknown factors (e.g. more frequently low molecular weight
age or obesity). heparin is given subcutaneously.
(Continued)