Page 430 - Essential Haematology
P. 430
416 / Chapter 30 Pregnancy and neonatal haematology
given to mothers in labour with very low platelet 120
counts or who are actively bleeding. Caesarean MCV 80
MCV
section may be indicated to protect the fetus. Nucleated red cells
Newborns of mothers with ITP should have a in blood for 4-7 days
20
blood count measured for the first 4 days of life as
the platelet count may progressively drop. A count 15
9
> 50 × 10 /L is reassuring. Cerebral ultrasounds Hb
may be performed to look for intracranial haemor- Haemoglobin (g/dL) Reticulocytes (%) 10
rhage (ICH). In newborns without evidence of
ICH, treatment with intravenous IgG is appropri- 5 Reticulocytes
9
’
ate if the infant s platelet count is < 20 × 10 /L.
Neonates with thrombocytopenia and ICH should 0
be treated with steroids and intravenous IgG 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
therapy. Months
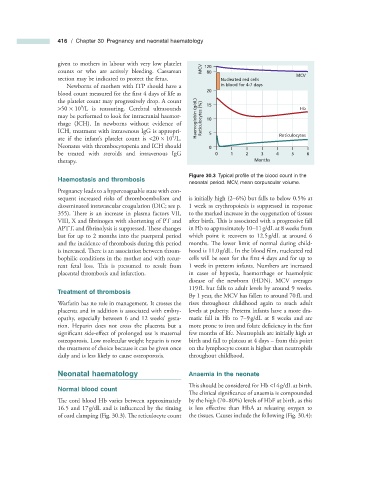
Figure 30.3 Typical profi le of the blood count in the
Haemostasis and t hrombosis
neonatal period. MCV, mean corpuscular volume.
Pregnancy leads to a hypercoaguable state with con-
sequent increased risks of thromboembolism and is initially high (2 – 6%) but falls to below 0.5% at
disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC; see p. 1 week as erythropoiesis is suppressed in response
355 ). There is an increase in plasma factors VII, to the marked increase in the oxygenation of tissues
VIII, X and fibrinogen with shortening of PT and after birth. This is associated with a progressive fall
APTT, and fibrinolysis is suppressed. Th ese changes in Hb to approximately 10 – 11 g/dL at 8 weeks from
last for up to 2 months into the puerperal period which point it recovers to 12.5 g/dL at around 6
and the incidence of thrombosis during this period months. The lower limit of normal during child-
is increased. There is an association between throm- hood is 11.0 g/dL. In the blood film, nucleated red
bophilic conditions in the mother and with recur- cells will be seen for the first 4 days and for up to
rent fetal loss. Th is is presumed to result from 1 week in preterm infants. Numbers are increased
placental thrombosis and infarction. in cases of hypoxia, haemorrhage or haemolytic
disease of the newborn (HDN). MCV averages
119 fL but falls to adult levels by around 9 weeks.
Treatment of t hrombosis
By 1 year, the MCV has fallen to around 70 fL and
Warfarin has no role in management. It crosses the rises throughout childhood again to reach adult
placenta and in addition is associated with embry- levels at puberty. Preterm infants have a more dra-
opathy, especially between 6 and 12 weeks ’ gesta- matic fall in Hb to 7 – 9 g/dL at 8 weeks and are
tion. Heparin does not cross the placenta but a more prone to iron and folate deficiency in the fi rst
significant side - effect of prolonged use is maternal few months of life. Neutrophils are initially high at
osteoporosis. Low molecular weight heparin is now birth and fall to plateau at 4 days – from this point
the treatment of choice because it can be given once on the lymphocyte count is higher than neutrophils
daily and is less likely to cause osteoporosis. throughout childhood.
Neonatal h aematology Anaemia in the n eonate
This should be considered for Hb < 14 g/dL at birth.
Normal b lood c ount
The clinical significance of anaemia is compounded
The cord blood Hb varies between approximately by the high (70 – 80%) levels of HbF at birth, as this
16.5 and 17 g/dL and is influenced by the timing is less effective than HbA at releasing oxygen to
of cord clamping (Fig. 30.3 ). The reticulocyte count the tissues. Causes include the following (Fig. 30.4 ):