Page 1130 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1130
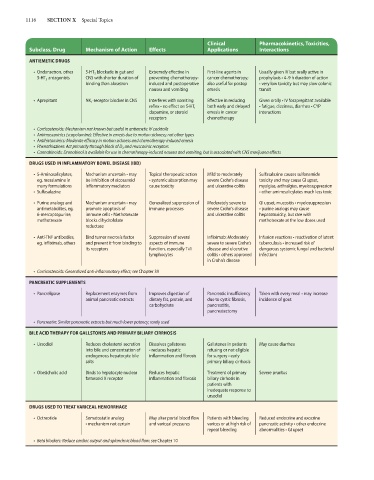
1116 SECTION X Special Topics
Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Toxicities,
Subclass, Drug Mechanism of Action Effects Applications Interactions
ANTIEMETIC DRUGS
• Ondansetron, other 5-HT 3 blockade in gut and Extremely effective in First-line agents in Usually given IV but orally active in
5-HT 3 antagonists CNS with shorter duration of preventing chemotherapy- cancer chemotherapy; prophylaxis • 4–9 h duration of action
binding than alosetron induced and postoperative also useful for postop • very low toxicity but may slow colonic
nausea and vomiting emesis transit
• Aprepitant NK 1 -receptor blocker in CNS Interferes with vomiting Effective in reducing Given orally • IV fosaprepitant available
reflex • no effect on 5-HT, both early and delayed • fatigue, dizziness, diarrhea • CYP
dopamine, or steroid emesis in cancer interactions
receptors chemotherapy
• Corticosteroids: Mechanism not known but useful in antiemetic IV cocktails
• Antimuscarinics (scopolamine): Effective in emesis due to motion sickness; not other types
• Antihistaminics: Moderate efficacy in motion sickness and chemotherapy-induced emesis
• Phenothiazines: Act primarily through block of D 2 and muscarinic receptors
• Cannabinoids: Dronabinol is available for use in chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, but is associated with CNS marijuana effects
DRUGS USED IN INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD)
• 5-Aminosalicylates, Mechanism uncertain • may Topical therapeutic action Mild to moderately Sulfasalazine causes sulfonamide
eg, mesalamine in be inhibition of eicosanoid • systemic absorption may severe Crohn’s disease toxicity and may cause GI upset,
many formulations inflammatory mediators cause toxicity and ulcerative colitis myalgias, arthralgias, myelosuppression
• Sulfasalazine • other aminosalicylates much less toxic
• Purine analogs and Mechanism uncertain • may Generalized suppression of Moderately severe to GI upset, mucositis • myelosuppression
antimetabolites, eg, promote apoptosis of immune processes severe Crohn’s disease • purine analogs may cause
6-mercaptopurine, immune cells • Methotrexate and ulcerative colitis hepatotoxicity, but rare with
methotrexate blocks dihydrofolate methotrexate at the low doses used
reductase
• Anti-TNF antibodies, Bind tumor necrosis factor Suppression of several Infliximab: Moderately Infusion reactions • reactivation of latent
eg, infliximab, others and prevent it from binding to aspects of immune severe to severe Crohn’s tuberculosis • increased risk of
its receptors function, especially Th1 disease and ulcerative dangerous systemic fungal and bacterial
lymphocytes colitis • others approved infections
in Crohn’s disease
• Corticosteroids: Generalized anti-inflammatory effect; see Chapter 39
PANCREATIC SUPPLEMENTS
• Pancrelipase Replacement enzymes from Improves digestion of Pancreatic insufficiency Taken with every meal • may increase
animal pancreatic extracts dietary fat, protein, and due to cystic fibrosis, incidence of gout
carbohydrate pancreatitis,
pancreatectomy
• Pancreatin: Similar pancreatic extracts but much lower potency; rarely used
BILE ACID THERAPY FOR GALLSTONES AND PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS
• Ursodiol Reduces cholesterol secretion Dissolves gallstones Gallstones in patients May cause diarrhea
into bile and concentration of • reduces hepatic refusing or not eligible
endogenous hepatocyte bile inflammation and fibrosis for surgery • early
salts primary biliary cirrhosis
• Obeticholic acid Binds to hepatocyte nuclear Reduces hepatic Treatment of primary Severe pruritus
farnesoid X receptor inflammation and fibrosis biliary cirrhosis in
patients with
inadequate response to
ursodiol
DRUGS USED TO TREAT VARICEAL HEMORRHAGE
• Octreotide Somatostatin analog May alter portal blood flow Patients with bleeding Reduced endocrine and exocrine
• mechanism not certain and variceal pressures varices or at high risk of pancreatic activity • other endocrine
repeat bleeding abnormalities • GI upset
• Beta blockers: Reduce cardiac output and splanchnic blood flow; see Chapter 10