Page 697 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 697
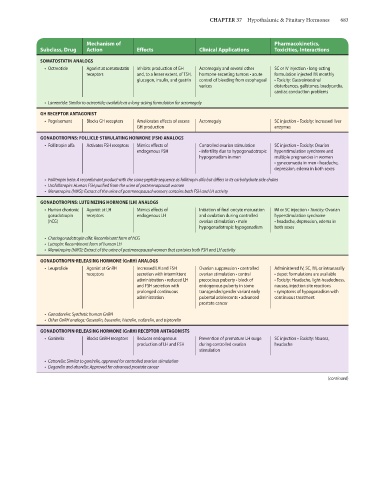
CHAPTER 37 Hypothalamic & Pituitary Hormones 683
Mechanism of Pharmacokinetics,
Subclass, Drug Action Effects Clinical Applications Toxicities, Interactions
SOMATOSTATIN ANALOGS
• Octreotide Agonist at somatostatin Inhibits production of GH Acromegaly and several other SC or IV injection • long-acting
receptors and, to a lesser extent, of TSH, hormone-secreting tumors • acute formulation injected IM monthly
glucagon, insulin, and gastrin control of bleeding from esophageal • Toxicity: Gastrointestinal
varices disturbances, gallstones, bradycardia,
cardiac conduction problems
• Lanreotide: Similar to octreotide; available as a long-acting formulation for acromegaly
GH RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST
• Pegvisomant Blocks GH receptors Ameliorates effects of excess Acromegaly SC injection • Toxicity: Increased liver
GH production enzymes
GONADOTROPINS: FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE (FSH) ANALOGS
• Follitropin alfa Activates FSH receptors Mimics effects of Controlled ovarian stimulation SC injection • Toxicity: Ovarian
endogenous FSH • infertility due to hypogonadotropic hyperstimulation syndrome and
hypogonadism in men multiple pregnancies in women
• gynecomastia in men • headache,
depression, edema in both sexes
• Follitropin beta: A recombinant product with the same peptide sequence as follitropin alfa but differs in its carbohydrate side chains
• Urofollitropin: Human FSH purified from the urine of postmenopausal women
• Menotropins (hMG): Extract of the urine of postmenopausal women; contains both FSH and LH activity
GONADOTROPINS: LUTEINIZING HORMONE (LH) ANALOGS
• Human chorionic Agonist at LH Mimics effects of Initiation of final oocyte maturation IM or SC injection • Toxicity: Ovarian
gonadotropin receptors endogenous LH and ovulation during controlled hyperstimulation syndrome
(hCG) ovarian stimulation • male • headache, depression, edema in
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism both sexes
• Choriogonadotropin alfa: Recombinant form of hCG
• Lutropin: Recombinant form of human LH
• Menotropins (hMG): Extract of the urine of postmenopausal women that contains both FSH and LH activity
GONADOTROPIN-RELEASING HORMONE (GnRH) ANALOGS
• Leuprolide Agonist at GnRH Increased LH and FSH Ovarian suppression • controlled Administered IV, SC, IM, or intranasally
receptors secretion with intermittent ovarian stimulation • central • depot formulations are available
administration • reduced LH precocious puberty • block of • Toxicity: Headache, light-headedness,
and FSH secretion with endogenous puberty in some nausea, injection site reactions
prolonged continuous transgender/gender variant early • symptoms of hypogonadism with
administration pubertal adolescents • advanced continuous treatment
prostate cancer
• Gonadorelin: Synthetic human GnRH
• Other GnRH analogs: Goserelin, buserelin, histrelin, nafarelin, and triptorelin
GONADOTROPIN-RELEASING HORMONE (GnRH) RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS
• Ganirelix Blocks GnRH receptors Reduces endogenous Prevention of premature LH surge SC injection • Toxicity: Nausea,
production of LH and FSH during controlled ovarian headache
stimulation
• Cetrorelix: Similar to ganirelix, approved for controlled ovarian stimulation
• Degarelix and abarelix: Approved for advanced prostate cancer
(continued)