Page 702 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 702
688 SECTION VII Endocrine Drugs
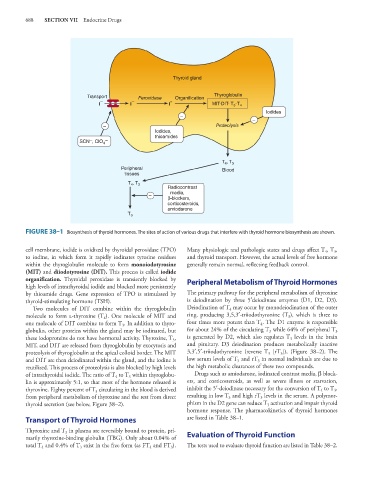
Thyroid gland
Transport Peroxidase Organification Thyroglobulin
I − I − I ° MIT-DIT- T 3 -T 4
Iodides
–
–
– Proteolysis
Iodides,
thioamides
– –
SCN , ClO 4
T 4 , T 3
Peripheral Blood
tissues
T 4 , T 3
Radiocontrast
media,
–
β-blockers,
corticosteroids,
amiodarone
T 3
FIGURE 38–1 Biosynthesis of thyroid hormones. The sites of action of various drugs that interfere with thyroid hormone biosynthesis are shown.
cell membrane, iodide is oxidized by thyroidal peroxidase (TPO) Many physiologic and pathologic states and drugs affect T , T ,
3
4
to iodine, in which form it rapidly iodinates tyrosine residues and thyroid transport. However, the actual levels of free hormone
within the thyroglobulin molecule to form monoiodotyrosine generally remain normal, reflecting feedback control.
(MIT) and diiodotyrosine (DIT). This process is called iodide
organification. Thyroidal peroxidase is transiently blocked by Peripheral Metabolism of Thyroid Hormones
high levels of intrathyroidal iodide and blocked more persistently
by thioamide drugs. Gene expression of TPO is stimulated by The primary pathway for the peripheral metabolism of thyroxine
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). is deiodination by three 5′deiodinase enzymes (D1, D2, D3).
Two molecules of DIT combine within the thyroglobulin Deiodination of T may occur by monodeiodination of the outer
4
molecule to form l-thyroxine (T ). One molecule of MIT and ring, producing 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine (T ), which is three to
3
4
one molecule of DIT combine to form T . In addition to thyro- four times more potent than T . The D1 enzyme is responsible
4
3
globulin, other proteins within the gland may be iodinated, but for about 24% of the circulating T while 64% of peripheral T
3
3
these iodoproteins do not have hormonal activity. Thyroxine, T , is generated by D2, which also regulates T levels in the brain
3
3
MIT, and DIT are released from thyroglobulin by exocytosis and and pituitary. D3 deiodination produces metabolically inactive
proteolysis of thyroglobulin at the apical colloid border. The MIT 3,3′,5′-triiodothyronine (reverse T [rT ]), (Figure 38–2). The
3
3
and DIT are then deiodinated within the gland, and the iodine is low serum levels of T and rT in normal individuals are due to
3
3
reutilized. This process of proteolysis is also blocked by high levels the high metabolic clearances of these two compounds.
of intrathyroidal iodide. The ratio of T to T within thyroglobu- Drugs such as amiodarone, iodinated contrast media, β block-
4
3
lin is approximately 5:1, so that most of the hormone released is ers, and corticosteroids, as well as severe illness or starvation,
thyroxine. Eighty percent of T circulating in the blood is derived inhibit the 5′-deiodinase necessary for the conversion of T to T ,
4
3
3
from peripheral metabolism of thyroxine and the rest from direct resulting in low T and high rT levels in the serum. A polymor-
3
3
thyroid secretion (see below, Figure 38–2). phism in the D2 gene can reduce T activation and impair thyroid
3
hormone response. The pharmacokinetics of thyroid hormones
Transport of Thyroid Hormones are listed in Table 38–1.
Thyroxine and T in plasma are reversibly bound to protein, pri-
3
marily thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). Only about 0.04% of Evaluation of Thyroid Function
total T and 0.4% of T exist in the free form (as FT and FT ). The tests used to evaluate thyroid function are listed in Table 38–2.
3
4
3
4