Page 698 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 698
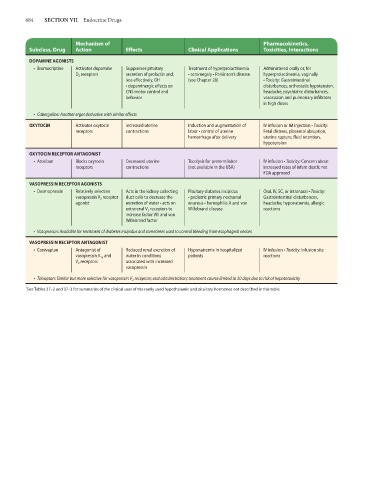
684 SECTION VII Endocrine Drugs
Mechanism of Pharmacokinetics,
Subclass, Drug Action Effects Clinical Applications Toxicities, Interactions
DOPAMINE AGONISTS
• Bromocriptine Activates dopamine Suppresses pituitary Treatment of hyperprolactinemia Administered orally or, for
D 2 receptors secretion of prolactin and, • acromegaly • Parkinson’s disease hyperprolactinemia, vaginally
less effectively, GH (see Chapter 28) • Toxicity: Gastrointestinal
• dopaminergic effects on disturbances, orthostatic hypotension,
CNS motor control and headache, psychiatric disturbances,
behavior vasospasm and pulmonary infiltrates
in high doses
• Cabergoline: Another ergot derivative with similar effects
OXYTOCIN Activates oxytocin Increased uterine Induction and augmentation of IV infusion or IM injection • Toxicity:
receptors contractions labor • control of uterine Fetal distress, placental abruption,
hemorrhage after delivery uterine rupture, fluid retention,
hypotension
OXYTOCIN RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST
• Atosiban Blocks oxytocin Decreased uterine Tocolysis for preterm labor IV infusion • Toxicity: Concern about
receptors contractions (not available in the USA) increased rates of infant death; not
FDA approved
VASOPRESSIN RECEPTOR AGONISTS
• Desmopressin Relatively selective Acts in the kidney collecting Pituitary diabetes insipidus Oral, IV, SC, or intranasal • Toxicity:
vasopressin V 2 receptor duct cells to decrease the • pediatric primary nocturnal Gastrointestinal disturbances,
agonist excretion of water • acts on enuresis • hemophilia A and von headache, hyponatremia, allergic
extrarenal V 2 receptors to Willebrand disease reactions
increase factor VIII and von
Willebrand factor
• Vasopressin: Available for treatment of diabetes insipidus and sometimes used to control bleeding from esophageal varices
VASOPRESSIN RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST
• Conivaptan Antagonist of Reduced renal excretion of Hyponatremia in hospitalized IV infusion • Toxicity: Infusion site
vasopressin V 1a and water in conditions patients reactions
V 2 receptors associated with increased
vasopressin
• Tolvaptan: Similar but more selective for vasopressin V 2 receptors; oral administration; treatment course limited to 30 days due to risk of hepatotoxicity
1
See Tables 37–2 and 37–3 for summaries of the clinical uses of the rarely used hypothalamic and pituitary hormones not described in this table.