Page 764 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 764
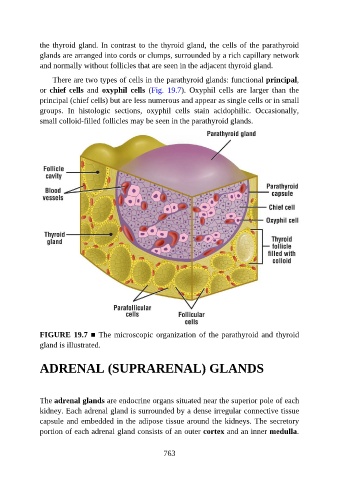
the thyroid gland. In contrast to the thyroid gland, the cells of the parathyroid
glands are arranged into cords or clumps, surrounded by a rich capillary network
and normally without follicles that are seen in the adjacent thyroid gland.
There are two types of cells in the parathyroid glands: functional principal,
or chief cells and oxyphil cells (Fig. 19.7). Oxyphil cells are larger than the
principal (chief cells) but are less numerous and appear as single cells or in small
groups. In histologic sections, oxyphil cells stain acidophilic. Occasionally,
small colloid-filled follicles may be seen in the parathyroid glands.
FIGURE 19.7 ■ The microscopic organization of the parathyroid and thyroid
gland is illustrated.
ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL) GLANDS
The adrenal glands are endocrine organs situated near the superior pole of each
kidney. Each adrenal gland is surrounded by a dense irregular connective tissue
capsule and embedded in the adipose tissue around the kidneys. The secretory
portion of each adrenal gland consists of an outer cortex and an inner medulla.
763