Page 769 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 769
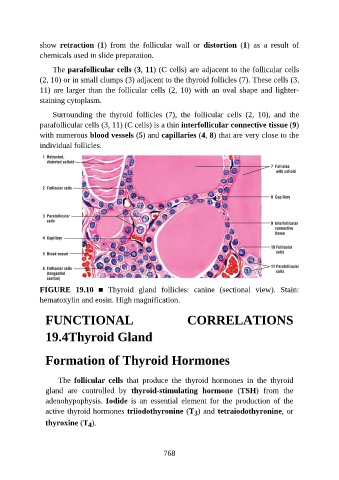
show retraction (1) from the follicular wall or distortion (1) as a result of
chemicals used in slide preparation.
The parafollicular cells (3, 11) (C cells) are adjacent to the follicular cells
(2, 10) or in small clumps (3) adjacent to the thyroid follicles (7). These cells (3,
11) are larger than the follicular cells (2, 10) with an oval shape and lighter-
staining cytoplasm.
Surrounding the thyroid follicles (7), the follicular cells (2, 10), and the
parafollicular cells (3, 11) (C cells) is a thin interfollicular connective tissue (9)
with numerous blood vessels (5) and capillaries (4, 8) that are very close to the
individual follicles.
FIGURE 19.10 ■ Thyroid gland follicles: canine (sectional view). Stain:
hematoxylin and eosin. High magnification.
FUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS
19.4Thyroid Gland
Formation of Thyroid Hormones
The follicular cells that produce the thyroid hormones in the thyroid
gland are controlled by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the
adenohypophysis. Iodide is an essential element for the production of the
active thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T ) and tetraiodothyronine, or
3
thyroxine (T ).
4
768