Page 391 - StudyBook.pdf
P. 391
Infrastructure Security: Devices and Media • Chapter 6 375
and making the overall network more manageable. In addition,VLANs can add
security to a network. By segmenting a network, administrators can isolate the
traffic going across each VLAN.This keeps the data flowing across one VLAN from
being visible to the other.Another vulnerability of switches is that there is a chance
for an attacker to override the security features provided by the switch. For
example, a DoS attack can be performed against some older switches similar to the
type that can be performed against a router.This can result in overloading of the
buffers in the switch, making it act like a hub and sending all data going through
the switch to all ports.This would then allow an attacker to sniff out data as if they
were connected to a hub rather than a switch. Keep in mind, this vulnerability only
affects older switches and should not be a problem with newer switches.
In addition, packets can be sent to a switch that can make it think an attacking
system is a different system on the network and cause it to route packets intended
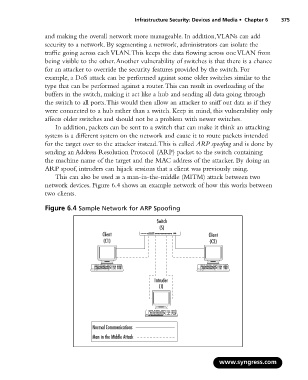
for the target over to the attacker instead.This is called ARP spoofing and is done by
sending an Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packet to the switch containing
the machine name of the target and the MAC address of the attacker. By doing an
ARP spoof, intruders can hijack sessions that a client was previously using.
This can also be used as a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack between two
network devices. Figure 6.4 shows an example network of how this works between
two clients.
Figure 6.4 Sample Network for ARP Spoofing
Switch
(S)
Client Client
(C1) (C2)
Intruder
(I)
Normal Communications
Man in the Middle Attack
www.syngress.com