Page 579 - StudyBook.pdf
P. 579
Public Key Infrastructure • Chapter 10 563
address the needs of the wider world, where there is perceived to be a need to trust
parties based on their assessment by a recognized authority.When I hire a techni-
cian to repair my heating unit, I want to know that he has been certified by the
state to do the work properly, without creating a lethal carbon-monoxide leak. For
more minor work, I’m comfortable knowing that he did a good job at a neighbor’s
house, using the Web-of-trust.This example demonstrates that the solution is to
create a Certification Authority (CA) who will vouch for credentials possessed by a
party to a trust.
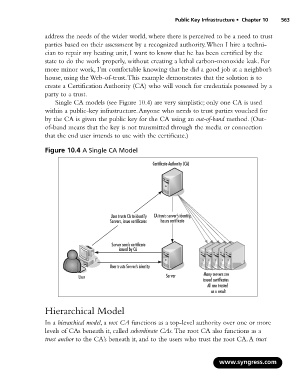
Single CA models (see Figure 10.4) are very simplistic; only one CA is used
within a public-key infrastructure.Anyone who needs to trust parties vouched for
by the CA is given the public key for the CA using an out-of-band method. (Out-
of-band means that the key is not transmitted through the media or connection
that the end user intends to use with the certificate.)
Figure 10.4 A Single CA Model
Certificate Authority (CA)
User trusts CA to identify CA trusts server’s identity,
Servers, issue certificates Issues certificate
Server sends certificate
issued by CA
User trusts Server’s identity
User Server Many servers are
issued certificates
All are trusted
as a result
Hierarchical Model
In a hierarchical model,a root CA functions as a top-level authority over one or more
levels of CAs beneath it, called subordinate CAs. The root CA also functions as a
trust anchor to the CA’s beneath it, and to the users who trust the root CA.A trust
www.syngress.com