Page 11 - Shroeder - Filter Systems
P. 11
Technical Cleanliness and
Contamination Management Basics
Consequences of
Particulate
Contamination
in Fluid Power
Systems
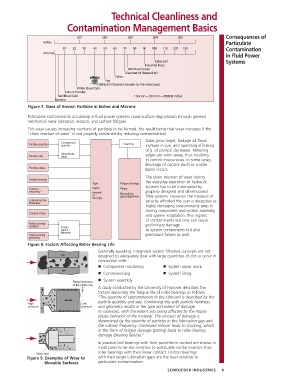
Figure 7. Sizes of Known Particles in Inches and Microns
Particulate contaminants circulating in fluid power systems cause surface degradation through general
mechanical wear (abrasion, erosion, and surface fatigue).
This wear causes increasing numbers of particles to be formed, the result being that wear increases if the
“chain reaction of wear” is not properly contained (by reducing contamination).
Gaps grow larger, leakage oil flows
increase in size, and operating efficiency
(e.g. of pumps) decreases. Metering
edges are worn away, thus resulting
in control inaccuracies. In some cases,
blockage of control ducts or nozzle
bores occurs.
The chain reaction of wear during
the everyday operation of hydraulic
systems has to be interrupted by
properly designed and dimensioned
filter systems. However, the measure of
security afforded the user is deceptive as
highly damaging contaminants seep in
during component and system assembly
and system installation. This ingress
of contaminants not only can cause
preliminary damage
to system components but also
premature failure as well.
Figure 8. Factors Affecting Roller Bearing Life
Generally speaking, integrated system filtration concepts are not
designed to adequately deal with large quantities of dirt as occur in
connection with:
■ Component machining ■ System repair work
■ Commissioning ■ System filling
■ System assembly
A study conducted by the University of Hanover describes the
factors impacting the fatigue life of roller bearings as follows:
“The quantity of contamination in the lubricant is described by the
particle quantity and size. Combining this with particle hardness
and geometry results in the type and extent of damage
to raceways, with the extent also being affected by the elasto-
plastic behavior of the material. The amount of damage is
determined by the quantity of particles in the lubrication gap and
the rollover frequency. Continued rollover leads to cracking, which
in the form of fatigue damage (pitting) leads to roller bearing
damage (bearing failure).”
In practice ball bearings with their punctiform contact are shown in
most cases to be less sensitive to particulate contamination than
roller bearings with their linear contact. Friction bearings
Figure 9. Examples of Wear to with their larger lubrication gaps are the least sensitive to
Movable Surfaces particulate contamination.
SCHROEDER INDUSTRIES 9