Page 51 - Human anatomy COMPLETELY DONE1
P. 51
dioxide in the blood between breaths;
the bodies of neurons whose processes form the vagus nerve;
centers of a number of protective reflexes (sneezing, coughing, vomiting), as well
as reflexes associated with digestion (swallowing, salivation).
The midbrain
Sometimes the so-called bridge of the brain is separately isolated from the
midbrain into an independent department.
On the surface of the midbrain, facing the cerebellum, there are four tubercles –
the quadrilateral.
The upper mounds of the quadrilateral are the centers of primary processing of
visual information, their neurons react to objects that move quickly in the field of
vision.
The lower mounds of the quadrilateral are the centers of primary processing of
sound information. The neurons of these centers respond to strong, sharp sounds,
bringing the auditory system into a state of heightened alert.
The most important motor centers are also located in the midbrain, participating
together with the cerebellum in maintaining muscle tone and coordinating body posture.
The impulses coming from the nuclei provide the ratio of the tone of the flexor and
extensor muscles.
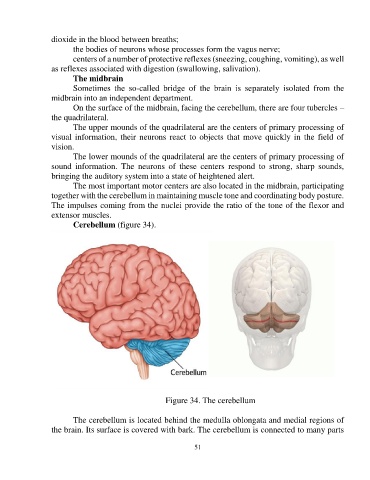
Cerebellum (figure 34).
Figure 34. The cerebellum
The cerebellum is located behind the medulla oblongata and medial regions of
the brain. Its surface is covered with bark. The cerebellum is connected to many parts
51