Page 102 - Deception at work all chapters EBook
P. 102
The Human Mind 43
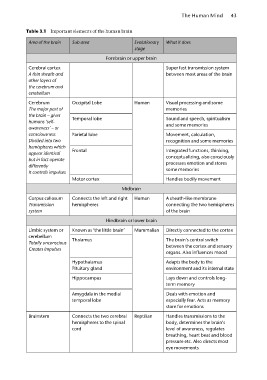
Table 3.1 Important elements of the human brain
Area of the brain Sub area Evolutionary What it does
stage
Forebrain or upper brain
Cerebral cortex Super fast transmission system
A thin sheath and between most areas of the brain
other layers of
the cerebrum and
cerebellum
Cerebrum Occipital Lobe Human Visual processing and some
The major part of Temporal lobe memories
the brain – gives Parietal lobe
humans ‘self- Frontal Sound and speech, spiritualism
awareness’ – or and some memories
consciousness Motor cortex
Divided into two Movement, calculation,
hemispheres which recognition and some memories
appear identical
but in fact operate Integrated functions, thinking,
differently conceptualizing, also consciously
It controls impulses processes emotion and stores
some memories
Handles bodily movement
Midbrain
Corpus callosum Connects the left and right Human A sheath-like membrane
Transmission hemispheres connecting the two hemispheres
system of the brain
Hindbrain or lower brain
Limbic system or Known as ‘the little brain’ Mammalian Directly connected to the cortex
cerebellum Thalamus
Totally unconscious The brain’s central switch
Creates impulses between the cortex and sensory
organs. Also influences mood
Hypothalamus Adapts the body to the
Pituitary gland environment and its internal state
Hippocampus Lays down and controls long-
term memory
Amygdala in the medial Deals with emotion and
temporal lobe especially fear. Acts as memory
store for emotions
Brainstem Connects the two cerebral Reptilian Handles transmissions to the
hemispheres to the spinal body, determines the brain’s
cord level of awareness, regulates
breathing, heart beat and blood
pressure etc. Also directs most
eye movements