Page 108 - Deception at work all chapters EBook
P. 108
The Human Mind 49
In all interviews we should consider using NLP and feedback techniques to our advantage.
The way of doing this is described later but you should always programme yourself when deal-
ing with suspected liars by imagining two monkeys on their backs.
More on channels of communication
PRINCIPLES
Primary channels of communication are normally aligned with the dominant hemisphere
of the brain. For example, right hemisphere-inclined people react better to visual input and
are less linear in their thought processes; they also react strongly (both positively and nega-
tively) to emotional and sensory stimuli. The language a person uses and his eye movements
(see Table 3.2, column 3) when processing and retrieving information will usually reveal his
primary channel of communication.
There is a very important point to note in relation to Table 3.2. It is that there is an excep-
tion to every rule. To test how a person reacts you should ask a few control questions, which are
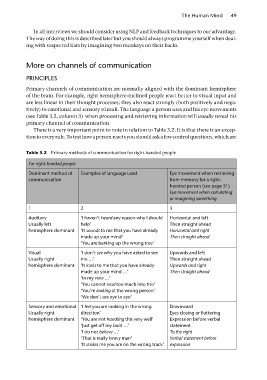
Table 3.2 Primary methods of communication for right-handed people
For right-handed people
Dominant method of Examples of language used Eye movement when retrieving
communication from memory for a right-
handed person (see page 51)
Eye movement when calculating
or imagining something
12 3
Auditory ‘I haven’t heard any reason why I should Horizontal and left
Usually left help’ Then straight ahead
hemisphere dominant ‘It sounds to me that you have already Horizontal and right
made up your mind’ Then straight ahead
‘You are barking up the wrong tree’
Visual ‘I don’t see why you have asked to see Upwards and left
Usually right me …’ Then straight ahead
hemisphere dominant ‘It looks to me that you have already Upwards and right
made up your mind …’ Then straight ahead
‘In my view …’
‘You cannot read too much into this’
‘You’re looking at the wrong person’
‘We don’t see eye to eye’
Sensory and emotional ‘I feel you are looking in the wrong Downward
Usually right direction’ Eyes closing or fluttering
hemisphere dominant ‘You are not handling this very well’ Expression before verbal
‘Just get off my back …’ statement
‘I do not believe …’ To the right
‘That is really heavy man’ Verbal statement before
‘It strikes me you are on the wrong track’ expression