Page 157 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 157
MECHANISMS FOR MOTION TRANSMISSION 143
mechanism identically apply here. This mechanism is widely used in low inertia, low load
force, and high bandwidth applications such as coil winding machines.
3.4 CYCLIC MOTION TRANSMISSION MECHANISMS
3.4.1 Linkages
One degree of freedom linkages define a nonlinear relationship between input and output
motion variables as
= f( ) (3.78)
out in
where is the input motion variable, out output motion variable, and f( ⋅ ) is the non-
in
linear geometric function. The position, velocity, and acceleration of the output variable
( (t), ̇ out (t), ̈ out (t)) are directly determined by the input variable ( (t)) and its time
out
in
̇
̈
derivatives ( (t), (t)) and the partial derivatives of the nonlinear function with respect
in
in
2
2
to the input variable ( f( )∕ , f( )∕ ).
in
in
in
in
Linkages are generally one degree of freedom, kinematically closed chain, robotic
manipulators. The motion of one member (output link) of the linkage is a periodic function
of the motion of another linkage member (input link). The most common linkages include
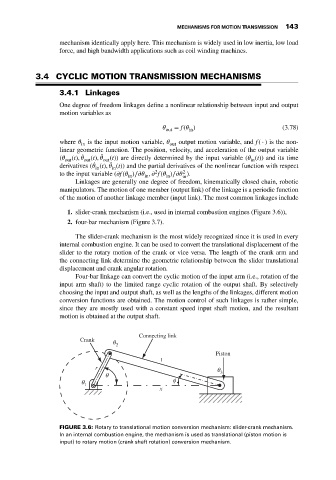
1. slider-crank mechanism (i.e., used in internal combustion engines (Figure 3.6)),
2. four-bar mechanism (Figure 3.7).
The slider-crank mechanism is the most widely recognized since it is used in every
internal combustion engine. It can be used to convert the translational displacement of the
slider to the rotary motion of the crank or vice versa. The length of the crank arm and
the connecting link determine the geometric relationship between the slider translational
displacement and crank angular rotation.
Four-bar linkage can convert the cyclic motion of the input arm (i.e., rotation of the
input arm shaft) to the limited range cyclic rotation of the output shaft. By selectively
choosing the input and output shaft, as well as the lengths of the linkages, different motion
conversion functions are obtained. The motion control of such linkages is rather simple,
since they are mostly used with a constant speed input shaft motion, and the resultant
motion is obtained at the output shaft.
Connecting link
Crank θ
2
Piston
l
r θ
θ 3
θ ϕ
1
x
FIGURE 3.6: Rotary to translational motion conversion mechanism: slider-crank mechanism.
In an internal combustion engine, the mechanism is used as translational (piston motion is
input) to rotary motion (crank shaft rotation) conversion mechanism.