Page 232 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 232
218 MECHATRONICS
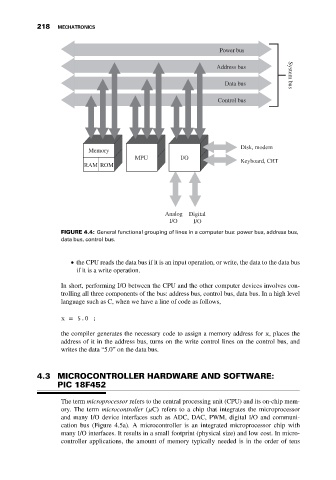
Power bus
Address bus
Data bus System bus
Control bus
Disk, modem
Memory
MPU I/O Keyboard, CRT
RAM ROM
Analog Digital
I/O I/O
FIGURE 4.4: General functional grouping of lines in a computer bus: power bus, address bus,
data bus, control bus.
the CPU reads the data bus if it is an input operation, or write, the data to the data bus
if it is a write operation.
In short, performing I/O between the CPU and the other computer devices involves con-
trolling all three components of the bus: address bus, control bus, data bus. In a high level
language such as C, when we have a line of code as follows,
x = 5.0 ;
the compiler generates the necessary code to assign a memory address for x, places the
address of it in the address bus, turns on the write control lines on the control bus, and
writes the data “5.0” on the data bus.
4.3 MICROCONTROLLER HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE:
PIC 18F452
The term microprocessor refers to the central processing unit (CPU) and its on-chip mem-
ory. The term microcontroller ( C) refers to a chip that integrates the microprocessor
and many I/O device interfaces such as ADC, DAC, PWM, digital I/O and communi-
cation bus (Figure 4.5a). A microcontroller is an integrated microprocessor chip with
many I/O interfaces. It results in a small footprint (physical size) and low cost. In micro-
controller applications, the amount of memory typically needed is in the order of tens